Contents
What is a wild yam plant?
Wild yam characteristics (Dioscorea villosa)
| Botanical classification | |
| Kingdom | Plantae |
| Subkingdom | Tracheobionta Vascular plants |
| Superdivision | Spermatophyta Seed plants |
| Division | Magnoliophyta or Angiosperms Flower plants |
| Class | Monocotyledons |
| Order | Dioscoreales |
| Family | Dioscoreaceae |
| Gender | Dioscorea |
| Species | D. villosa |
Common English name:Wild yam, Yam, Colic root, Devil’s bones, Rheumatism root, American Yam, Atlantic Yam, Barbasco, China Root.
– Spanish: ñame silvestre, raíz del cólico
– Catalan: nyam silvestre
– French: igname
– Euskara: nyama
– Portuguese: inhame
– Italian: batata
– German: Yamswurzel

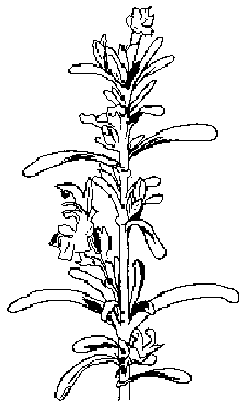
In the picture: botanical illustration of yam plant. This can achieve up to 3m. tall
Scientific name: Dioscorea villosa L.
Etymology: the genus Dioscorea refers to the Greek physician and botanist Dioscorides, the species name, villosa, refers to the appearance of rough hairs on the leaves.
Family: Dioscoreaceae
Origin: at present, there are over 600 species of yam (Dioscorea spp.). It is difficult to determine their origin, although it is believed that wild yam is native to North America.
Wild yam description
Wild yam (Discorea villosa) is a perennial plant, with tuberous roots, which grow feral in North America, near lakes, swamps, humid forests and hillsides. It grows at altitudes from sea level to 1,500 m.
It is a climbing plant with thin stems up to 3m. high, with spines on the leaf axils.
The leaves are large, 13cm. long, alternate, heart-shaped and acuminate at the apex. On the limb 8 veins are marked. limbo has fine pubescence on the back.
The plant produces tubers and bulbils (aerial tubers), which arise from the leaf axils. These are cylindrical and rich in carbohydrates, which enable the plant to survive in very dry climates.
Flowers appear from September to October. It is a dioecious plant, with male flowers and female flowers, which open at different times, which makes pollination and fertilization of the plant very difficult. For this reason, the yam can not produce seeds.
It presents thickened root tubers. They can weigh up to 10kg., being rich in starch and containing diosgenin, a saponin type used for the manufacture of drugs.
The fruit is a capsule, 1.5-2.5 cm. in length, that reserve inside the plant seeds, 7-14mm.
Used parts of yam
- Tubers.
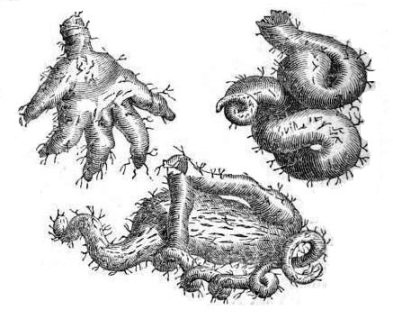
In the image: tubers of wild yam
Uses of wild yam
- Production of pharmaceuticals: wild yam is rich in steroid saponins, which through laboratory processes get converted into raw material for manufacturing oral contraceptives, hormones and cortisone. However, populations of wild yam are hard to find, so also two species of Dioscorea are also grown for pharmaceutical purposes (D composita and D. floribunda).
- Medicinal: the plant is used for medicinal purposes.
* More information about the medicinal properties of yam in the links below
Active components of wild yam
- Saponins: wild yam has a high content of steroid saponins: dioscin, dioscorin and diosgenin. These substances are toxic when consumed in high doses, but, in controlled amounts, they can have health benefits as anti-inflammatory, soothing, hepatoprotective and cholesterol.
- Vitamins: supplement rich in B vitamins, especially thiamine and niacin.
- Minerals: potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, sodium, iron, zinc, chromium, cobalt, silicon, boron, manganese.
![]() More information about wild yam
More information about wild yam