Contents
What is a vitex plant?
Characteristics of vitex (Vitex agnus-castus)
Common English name: Chaste tree, Monk’s pepper, Lilac chastetree, vitex
It is thought that its name comes from the fact that people in the past considered this tree to posses anaphrodisiac properties since it inhibited the desire. In fact its fruits were used by the medieval religious men to eliminate sexual desire. Although in other moments it has also been used for the opposed purpose. Its scientific name refers to the symbol of chastity since agnus-castus in Latin means “chaste lamb”.
Scientific name: Vitex agnus-castus L.
Family: Vervain family – Verbenaceae
Habitat: By the streams and humid places of central Asia and the Mediterranean. Albania and Morocco are the main producers of the world.
Description of Vitex
Deciduous bush of the vervain family up to 6 m when it is cultivated, although in wild state it doesn’t attain more than 3.
Scented leaves with very long petioles till 10 cm, palmate-compound with 5-7 leaflets, green above, gray pubescent below.
Flowers in spikes, violet or purple that grow in summer on the new branches developed during spring.
Eatable fruits, black or reddish.
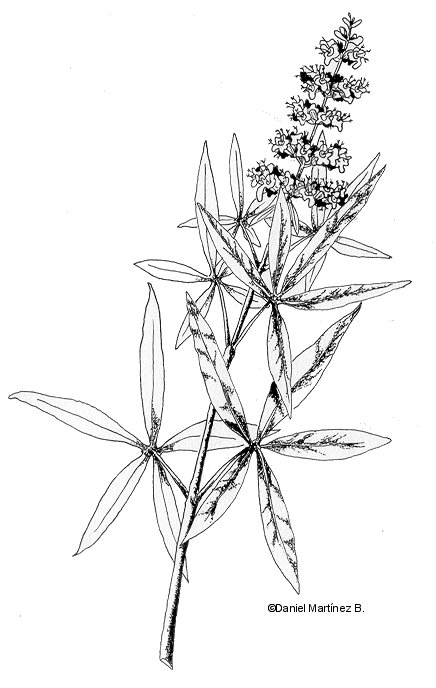
A drawing of chaste tree with flowers and leaves
Components of vitex
- Iridoid Glycosides: Agnuside and aucubin (Fruits and leaves)
- Fat (fruits)
- Casticin (Leaves)
- Progesterone (Leaves)
- Testosterone (Leaves)
- Essential oils: Alpha-terpineol, cineol, camphene, beta-pinene, beta-caryophyllene, beta – farnesene, beta-phellandrene, limonene, myrcene, sabinene (Leaves)
![]() More information on vitex toxicity, contraindications and side effects.
More information on vitex toxicity, contraindications and side effects.








