Contents [show]
ANOTHER TYPES OF STEMS
There are some special types of stems. The most important are:
Underground stems:
|
|
|
Rhizomes are stems that grow horizontally under the surface of the ground. From them roots are born, moving downwards into the ground and other herbaceous stems follow the opposite way searching the air. So, apart from storing food, they are a way of plant propagation. Canes would be a good example of them.
Tubers are expanded stems by accumulation of food for the plant, such as the potato or the tulip bulbs.They have buds where new plants grow. (More information: Types of tubers)
Bulbs are in fact buds adapted to leave under the ground, that store food provisions. Onions are bulbs.
Succulent stems
They become very fat because of water accumulation. They use it as a reservoir for the long dry periods they have to stand. They are so well adapted to the environment that they have transformed their leaves into prickles, which besides increasing water provision, help the plant to keep herbivores out of range. Cacti are included in this group.
Above-ground stems:
They do not grow below the ground but on the surface or very near to it. The most important are
STOLONS
These are weak spreading stems, running along the surface of the ground and producing new plants from their nodes. Strawberries belong to this group.
VINES
Stems that grow on the ground surface till they find something to get upright. They are slender, with long internodes. They can achieve their goal by means of:
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|

Photo of ivy climbing up a tree trunk.
More information on climbing plants
Other stems:
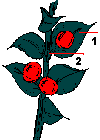
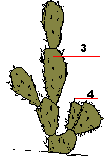
| The leaf-like cladodes (Phylloclades) and cladodes are leaflike stems. They appear because the real leaves are very small, therefore non functional. Two clear examples are the butcher’s broom and the prickly pear. |
|
| 1) leaf-like cladodes. 2) real minute leaves. 3) cladodes 4) leaves developed to prickles. |
Questios of stems

Select the correct answer for each question:

This cactus shows:
A herbaceous stem
Cladodes
A rhizome
The plant of the picture has:
A ligneous stem
A leaf-like cladode
A tuber

You think this plant is:
A shrub
A bush
A herbaceous plant
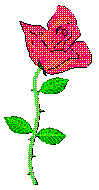
This plant shows:
Stolons
Flexible climbing stems
Climbing prickly stems
 Go back to main page “The stems”
Go back to main page “The stems”
To know more about “The stems”
![]() More information about plant cultivation.
More information about plant cultivation.


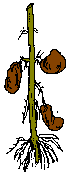


 Correct!
Correct!