Contents
What is a saffron plant?
Characteristics of saffron plant (Crocus sativus)
Common English name: saffron, Spanish saffron, cultivated crocus
Etymology: ” Saffron ” from the Arabic ” safra ” meaning yellow.
Scientific name: Crocus sativus L.
Etymology: Crocus derived from Greek and means ” thread” [ tissue ], referring to the appearance of the stamens.
Family: Iridaceae
Origin: It is believed that this plant is native to Iran, specifically from Alvand in the Zagros Mountains.
Habitat: Bare, sunny and treeless terrain. Is generally cultivated, or in places where it has been cultivated once.
It is a sterile plant, so it is not found in the wild, but in places where someone has planted the bulbs. it requires regions with cold winters and hot summers, fitting different latitudes and temperatures. Resistant to frost.
Geographical Distribution: native to eastern Asia, this plant is naturalized throughout the Mediterranean region, North Africa, India and China.
Botanical description of saffron
Saffron or Crocus (Crocus sativum) is a perennial plant native to Iran since ancient times and naturalized throughout the Mediterranean region and East Asia.
This plant is low-rise, from 10 to 25cm., Developed from corms.
A corm is a bulbous tuberous structure, 2.5 -3cm. in diameter, with whitish coated fibers and earthy color.
The saffron bulb has a reproductive function, since it grows up every year after losing his aerial part in winter. Each bulb every year forms 2 or 3 new ones.
The crocus bulb has adventitious roots, from where leaves and flowers of the plant will be born.
Like all plants of the genus Crocus, saffron has attractive flowers, popularly called ” saffron rose”
The crocus flower is solitary and terminal, purplish and consists of 6 petals, three stamens, and a style ending in three red-orange stigmas.
Unlike other flowers of the same gender, crocus flowers do not close during the night.
The stigmas of the plant are the part that arouses greater commercial interest because of their coloring. The stigmas of this species, also called strands, pistils of saffron or saffron threads, are particularly long, measuring between 20 and 50mm.
Saffron flowers appear in September or October, and they are open for only two or three days. It is said that the stigmas must be harvested early in the morning, before sunrise.
After flowering, the plant leaves appear in late autumn or winter, and persist until spring.
The leaves are stemless (they are devoid of stem), sheathed, with narrow ciliate margins, dark green. Its leaves are characterized by a longitudinal white line in the middle.
In a saffron plant, there can be between 4 and 10 leaves, very narrow and long, about 2mm. in width, and 10 – 20cm. long.
Being triploid, this plant is necessarily sterile, the plant reproduces by bulbs. This kind of saffron, being sterile, does not produce fruits.
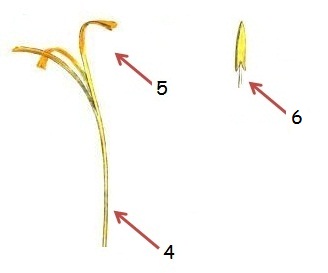
Parts of the saffron flower: long style (4), completed in three stigmas (5), and the
What parts of saffron flower are used?
– Stigma of the flower when the crocus flower opens, the flowers are picked one by one by hand. Each saffron flower has three stigmas, which must be plucked by hand. Stigmas are orange-red. They pass through a drying process in which they lost four-fifths of their weight, so as to get 1kg. of dry saffron is needed to harvest 120,000 crocus flowers.
These stigmas of saffron are one of the most popular food coloring, being the only spice that is sold per gram and the most expensive one.
Precisely because of its expensive price, this spice is often adulterated with stigmas of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius) or with other flowers, cut to form threadlike, and stained with tartrazine. Adulteration have also been reported with lead or other minerals. For these reasons, it is important to acquire this valuable spice in local trusted premises and with checked packaging.
– Flower Petals: until recently, after collecting the stigmas of the flower, the nutritional value of other parts of the plant was dismissed. Recent studies have shown that saffron petals contain large quantities of anthocyanins. Saffron is being considered in the industry as a potential source of food coloring, also not toxic to health.
– Stamens or ” Crocus little birds “. Crocus flower contains 3 yellow stamens, which are the male organ of the flower. They contain pollen sacs (anthers), which can also be commercialized as dye and for aromatic purposes.
– Leaves: The leaves of the plant are used for animal fodder (sheep and goats). Scientific studies have found that this food presents a good digestibility and increases milk secretions of ruminants. However, it is necessary to supplement it with protein to improve its quality.
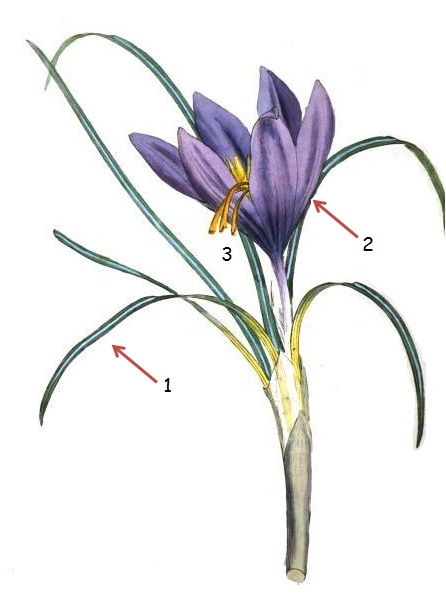
Botanical illustration of a saffron plant (Crocus sativus). You can see the leaves of the plant, with a characteristic white line (1), the six petals of the flower (2) and the long stigmas of the plant (3), hovering the corolla.stamen, where the anther or pollen sac (5).
Crocus species
– Wild crocus (Crocus cartwrightianus) native plant from Greece and Crete, it is believed to be the precursor of the current crocus species (Crocus sativus), the latter of triploid nature and therefore sterile. Wild saffron can be found in nature and spreads by seeds.
– Spring crocus or giant crocus (Crocus vernus): botanically, differs from Crocus sativus because its style is split into three parts. This is not a medicinal species. It blooms in spring and, at the same time, it produces its foliage.
– Albertino Saffron (Crocus versicolor) It can be found in Alberta (Canada), in South East of France and North West of Italy, blooming in spring. Mainly used for ornamental gardens.
Crocus sativus has Not to be confused with autumn saffron, also called meadow saffron or naked lady, (Colchicum autumnale), which is a very toxic plant.
![]() Continue reading… Saffron properties
Continue reading… Saffron properties
| Botanical classification of saffron | |
| Kingdom | Plantae |
| Subkingdom | Tracheobionta Vascular plant |
| Superdivision | Spermatophyta Seed plants |
| Division | Spermatophyte |
| Subdivision | Angiosperms |
| Class | Liliopsida or Monocotyledonous |
| Subclass | Coroliferous |
| Order | Liliales |
| Family | Iridaceae |
| Tribe | Croceas |
| Subtribe | Crocinas |
| Gender | Crocus |
| Species | C. sativa |








