Classification of a root
|
|
|
|
|
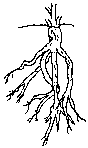
Taproot, It is the primary root from which secondary roots (rootlets) derive from.
Fibrous roots do not have a primary root. They show almost the same size and width.
Elongated taproots offer a very fat primary root because they accumulate food it.
Tuberoid roots or tuberous roots are fibrous roots that became fat because of the accumulation of nutrients. (More information)
Branched roots do not have a primary root. They resemble to the branches of a tree.
Other types of roots
Besides the more usual roots named above, we should consider those ones that are a bit special. Those not inserted into the soil, either because they are in the open air or because they live inside the water. These special roots are the following:
Adventitious roots | ||
 |
| |
| Those who grow from a stem and are used by some plants to spread along the surface of the soil. | ||
Water roots | ||
| ||
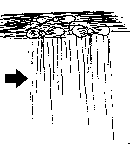
| Those living in the water. | ||
Parasite roots | ||
| ||
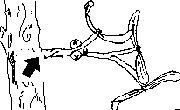
| They are stuck on another plant, sucking the nutrients from it.The mistletoe is a clear example of this type. | ||
Questions about root

Choose the suitable answer:

The carrot has a:
Typical root
Taproot
Taproot

The chive has a root:
Axonomorph
Fasciculate
Napiform
A parasite root aims mainly
To stick the plant to the soil
To suck nutrients from the soil
To absorb nutrients from another plant
Ivy has some roots:
Axonomorph
Parasite
Fasciculate
 Go back to main page of “The roots”
Go back to main page of “The roots”
![]() More information about plants cultivation.
More information about plants cultivation.
6 December, 2020

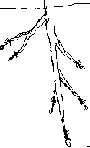

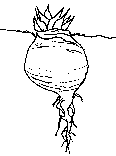
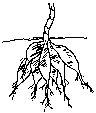
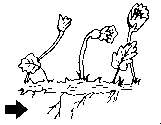
 Correct!
Correct!