Contents
Characteristics of rapeseed
What is a rapeseed?
– Common English name: Rapeseed, rape, oilseed rape, rapa, rappi, rapaseed
– Spanish / Español: Colza, rutabaga, vainitas, nabillos, mostacillas, nabos aceiteros, canola

– Scientific name: Brassica napus L.
– Family: Cruciferae plants
Origin. Where to find rapeseed plants?
Its origin is unknown . It is found mainly in Central and Southern Europe and in Western Asia. Sometimes wild specimens come from a crop escape. It arrived in Canada in 1942, when it was then used as a lubricant for warships.
It is cultivated in many places , being a productive and economic crop, of rapid growth, which offers a wide range of possibilities for use. It resists frost, requiring an annual rainfall of 400mm and a temperature between 5 and 27ºC.
It does not tolerate waterlogging, needing deep and well-drained soils. Soil reaction or pH: 6.2 (from 4.2 to 8.2).
Distribution: cultivated in most European countries, naturalized in the majority.
The main producers are USA, China, Germany, Italy, France, Japan, India, United Kingdom, Austria, Bangladesh.
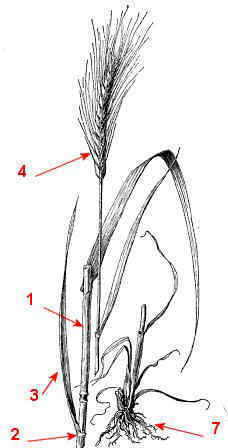
Description of rapeseed
Annual plant, sometimes biennial – when the planting is late, it blooms the following year- with a erect and branched stem, measuring between 0.5m. and 1,70m.
Pivotal or main root, tuberose and fusiform. The leaves are petiolate, glaucous (dark green-bluish), glabrous (without villus) and soft touch. The basal leaves are lyrate-pinnatifid, while in the upper part of the plant, they are oblong-lanceolate, thin, hugging the stem and sessile.
The inflorescence is a terminal cluster of yellow flowers, characteristic of the Cruciferae, with petals arranged in the shape of a cross. They are hermaphroditic and pollinated by insects like bees.
Flowers between May and August.
The fruit is a silicua, 5-11cm. long by 2.5-4mm. Wide. Inside contains between 15 and 40 seeds.
Study of rapeseed and Canola

Rapeseed (Brassica napus) is a plant of the Cruciferae family that is used to obtain oil, because the seeds have richness in oil (between 35-45% of fats).
Initially, oil extracted from rapeseed was not considered fit for human consumption, because it contained high amounts of erucic acid and glucosinolates:
- Erucic acid is a type of toxic fat found in the seeds and oils of Cruciferae plants.
- Glucosinolates are also present in the whole family of Cruciferae, and are responsible, for example, for the spicy taste of cabbage, mustard or radish. These substances, in high doses (as in an oil), can have anti-nutritive effects.
However, towards the 1970s, work was done to discover new varieties of rapeseed with a lower level of these toxic substances.
It was in the 70’s when the Canola was patented. The name canola comes from the acronym in English: Canadian oil low acid; name patented in Canada in 1978, which describes a series of plants with standard contents of erucic acid and glucosinolates, suitable for the production of edible oil.
Currently, canola oil has less than 2% erucic acid, and a minimum content of glucosinolates. The oil obtained is used in food as a source of essential fats, and industrially, to make margarine.
What parts of rapeseed are used?
From rapeseed, we use : Roots, leaves, flowers, seeds.
Uses of rape seed
- Canola oil: the seeds are rich in oil (up to 45%), rich in monounsaturated fats and linoleic acid (see composition). This oil is used as a lubricant, for the manufacture of soap and detergents, for fuels and biodiesel, in the food and food industry, and for lighting torches. Erucic acid is also extracted from this, which is used to make other chemical products.
- Food: only if they are free of pesticides, you can take the leaves and flowers of the plant as food. Rapeseed leaves are consumed in salads. The bouquets of immature flowers can be consumed like broccoli. The sprouts are consumed in salads and to flavor mustard sauces. The oil is used in food as food oil, in salads, ice-creams , cakes and breads.
- Medicinal: the root is medicinal, and is used as a diuretic, emollient, expectorant and against rheumatic pains.
- Honey: the production of canola also allows the beekeeping of the crop, since it is a honey plant.
- Animal fodder: the plant serves as fodder for animals, source of vegetable proteins. It is a cheap, fast and productive crop. The main fodder interest rests on the roots, although the leaves are also used. This is very watery (85-90%), with high digestibility (90%), but poor in proteins. Feeding with high doses of this type of fodder in cows can transmit bad taste to the milk. There are crops dedicated to this use, known as forage rape.
- Green manure: like all cruciferous plants, this plant is a good green winter manure.
Composition of rapeseed
The plants of the rape family stand out for having components called glucosinolates. These substances provide the characteristic spicy flavor to mustard or cabbage.
- The seeds are rich in oil (up to 45%). They contain six glycosides: gluconapine, glucobrassicanapine, glucocortin, gluconasturtine, glucorapiferin (progoitrin) and sinalbine. The enzyme myrosinase is present.
- The plant is rich in mucilage.
- The roots are rich in carbohydrates, although their high water content makes them a very hypocaloric vegetable. They contain allantoic acid and allantoin with healing properties.
- It is a very suitable food in weight loss diets, gastritis, ulcers, for people with cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.
- Natural antioxidant pigments: betacarotenes in leaves and flowers.
Components of rapeseed
| Components of rapeseed per 100g. | |||
Nutrient | Root | Leaves | Flowers |
Calories (kcal.) | 46 | 61 | 37 |
Carbohydrates (g.) | 11 | 11,2 | 6,4 |
Proteins (g.) | 1,1 | 2,9 | 4,3 |
Fats(g.) | 0,1 | 1,7 | 0,4 |
Fiber (g.) | 0,8 | 1,8 | 1,5 |
Vitamin C (mg.) | 43 | 120 | 42 |
Vitamin B1 or thiamin (mg.) | 0,07 | 0,08 | 0,04 |
Vitamin B2 or riboflavin (mg.) | 0,07 | 0,15 | 0,02 |
Vitamin B3 or niacin (mg.) | 1,1 | 0,5 | 1,2 |
Betacarotenes (Eq. mg.) | – | 2.680 | 3.200 |
Calcium (mg.) | 66 | 136 | 117 |
Phosphorus (mg.) | 39 | 38 | 97 |
Iron (mg.) | 0,4 | 4,6 | 3,4 |
Water (g.) | 87 | 83,3 | 87,4 |
![]() More information on rapeseed
More information on rapeseed