Contents
- 1 What is a pumpkin plant?
- 1.1 Characteristics of pumpkins (Cucurbita pepo)
- 1.2 What are pumpkin plants like?
- 1.3 How to distinguish male and female flowers:
- 1.4 How are the fruits of pumpkin plant?
- 1.5 Which is the biggest pumpkin?
- 1.6 HISTORY AND FOLKLORE OF PUMPKINS
- 1.7 Origin of pumpkins
- 1.8 Pumpkins in Europe
- 1.9 Pumpkins in the culture of many places
- 1.10 Pumpkins crust to make musical instruments
- 1.11 Composition: Active components of pumpkin
What is a pumpkin plant?
Characteristics of pumpkins (Cucurbita pepo)
Common noun: Pumpkin, Vegetable marrow, Field pumpkin
Scientific noun: Cucurbita pepo L.
Family: Gourd family – Cucurbitaceae
Habitat: Native from Central America and cultivated in many parts of the world.
Pumpkins are the fruits of the gourd (Cucurbita) a creeping plant of the family of the cucurbitaceae, which includes other fruits such as melon (Cucurbita melo), watermelons (Citrullus vulgaris), cucumber (Cucumis sativus) and other wild as the exploding cucumber (Ecballium elaterium)
 .
. 
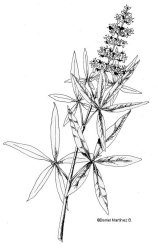
Botanical illustrations of the leaf and fruit of a pumpkin
What are pumpkin plants like?
Pumpkin plants are creeping herbs up to 10 m. in length.
Stems hairy, grooved, hollow inside.
Leaves cordate, lobed
Flowers unisexual, up to 10 cm. with the cup attached to the corolla, stamens, the male soldiers in the column.
Pumpkin fruits are pepos. These pepo fruits vary in different shapes and colors according to the different varieties that can reach over 30 kg. The immature fruits are called courgettes.
How to distinguish male and female flowers:
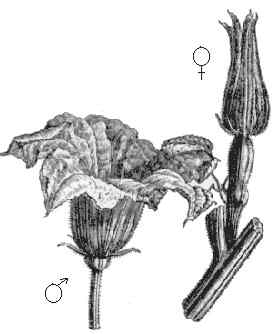
Detail of male and female flowers
How are the fruits of pumpkin plant?
Fruit in pepo very variable of different shapes or colors according to the different varieties that can reach more than 30 kg in weight.

Which is the biggest pumpkin?
There are world contests of giant pumpkins. They belong to the species Retort principle. The world’s largest pumpkin in this species won a contest in the southern town of Manchester in USA in 2002 and weighed 606 kg)

HISTORY AND FOLKLORE OF PUMPKINS
Origin of pumpkins
Cultivation of pumpkins approximately starts back in the year 5000 BC in different parts of the world. It appears in the territory that now constitutes Mexico, before the emergence of civilization known as the Olmecs, Mayas and Aztecs.
These early cultures settled in the area and based their existence on the cultivation of squash, corn, beans and peppers. We also have archaeological references from the same period in the Yangtze Valley in China in a civilization that crops mainly rice and squash.

Pumpkins can be very different in size or form
Pumpkins in Europe
Spanish settlers were those who learned to cultivate in their contact with the natives and then brought to Spain, where its cultivation spread to other parts of Europe with temperate or warm climate.
There are smaller varieties, mainly devoted to the cultivation of squash, which can be grown anywhere in the world since withstand any climate.
In addition to food, in the excavations of prehistoric remains have been found spoons or containers made with pumpkin peel. Gourds have been used to carry out some old musical instruments. For example, prehistoric sites have been found in India 4500 years ago in which bells are made with pumpkins empty inside which were placed dry seeds.

Some pumpkins are cultivated because of their extraordinary forms
Pumpkins in the culture of many places
Gourd is part of the traditional folklore of many people. Thus we have the Halloween pumpkins which fruit is the material for faces that are illuminated by placing lighted candles inside, forming what is known as “Halloween lanterns.” (Almost all U.S. production is intended for the manufacture of this type of lantern)
A wine-saving pumpkin was one of the elements that formed part of the team of the pilgrims on the Camino de Santiago.
In Haiti, in 1800, these fruits were declared the official currency of the country. Subsequently “gourde” was the name given to the currency of this country and this word comes from the English word “gourd” meaning pumpkin.
Pumpkins crust to make musical instruments
Pumpkin crust has been used as the raw material to make musical instruments in many places. For example:
- In traditional Chinese music, pumpkin was one of the first materials used in the manufacture of instruments
- The “carimba” is an Nicaraguan and Costa Rican instrument which resonance box consists of a pumpkin.
- The original banjo, which was imported from Africa to the U.S. by African slaves, was based on a pumpkin.
- The first maracas were made by tying a stick to this fruit, inside which were placed plant seeds. In reality, those derived from rattles and primitive made with the same method.
Composition: Active components of pumpkin
- Amino acids: alanine, arginine, cucurbitin, cystine, glycine, histidine, isoleucine, lysine. (Fruits and seeds)
- Acids: linoleic, aspartic, oleic and palmitic (Flowers, fruits and seeds)
- Vitamins: vitamin A and vitamin B (Niacin, Thiamin) (Flowers, fruits and seeds)
- Fats: lecithin (seeds)
- Fibers (fruits and seeds)
- Minerals: calcium, cobalt, boron, magnesium, zinc, potassium, iron…(fruits)
- Sugars: sucrose.
* Related information:
![]() More information on pumpkin.
More information on pumpkin.