Contents
SYMMETRY IN PLANTS
What is symmetry?
Symmetry can be defined as similarity, or balance among systems or parts of a system. This word derives from Latin symmetria, which in turn comes from Greek summetria (=proportion). The following pictures are considered symmetric
Symmetry types in plants
Plants parts, as many living organisms, also present symmetry. The symmetry in plants can be:.
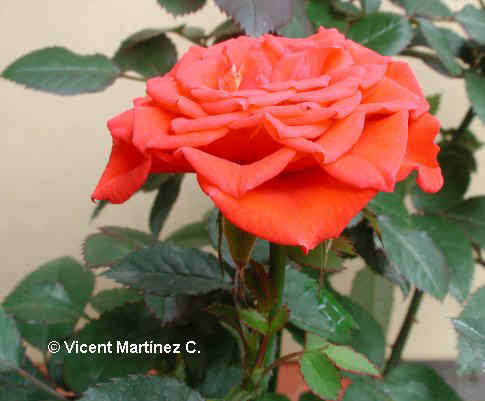
- Radial symmetry: This a type of symmetry resulting from a plant being cut along a line passing through the center of an imaginary circumference (the diameter). In this case, the two resulting parts are identical.
This type of symmetry is very frequent in fruits, stems and flowers (actinomorphic flowers) such as those of rosaceae,
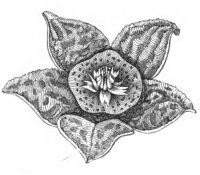
Radial symmetry in a flower
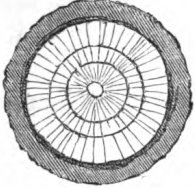
Radial symmetry in a stem
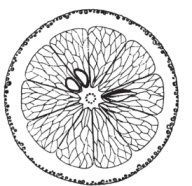
Radial symmetry in a fruit
- Bilateral symmetry: This a type of symmetry that occurs when only two faces are the same. The plant part can only have a single plane (the sagittal plane) that divides it into two exact parts.
This type of symmetry takes place in many flowers, leaves and in cactus stems
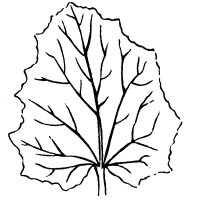
Bilateral symmetry in a leaf
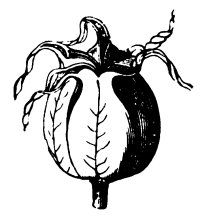
Bilateral symmetry in a fruit

Bilateral symmetry in a cactus stem
- Dorsiventral symmetry: It is considered as the real bilateral symmetry. This differs from previous symmetry in the fact that front side is different from back side, so only left and right sides are the same.
Dorsiventral symmetry is present in most leaves and in some flowers (Zygomorphic) such as those of labiatae,
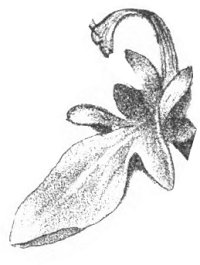
Dorsiventral symmetry in a flower

Dorsiventral symmetry in a leaf
Activities and exercises: What do you think?
What type of symmetry do the following plants parts have?

Bulb of hyacinth
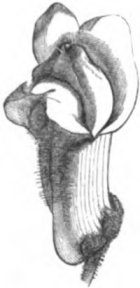
Snapdragon flower
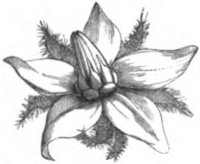
Borage flower

Hollyhocks pollen
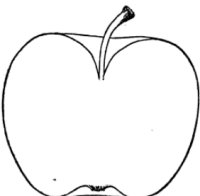
Apple
![]() More information about leaves and stems
More information about leaves and stems