Contents
What is a pecan?
Characteristics of pecan (Carya illinoinensis)

Common English name: Pecan,, pecan hickory, pecan sweet, Illinois nut, soft-shelled hickory, Pecan nut
Scientific name: Carya illinoinensis (Wangenh.) K. Koch.
Etymology: the scientific name is a composition of “Carya”, the Greek name of walnut, and “illinoinensis”, which refers to Illinois, US state
Taxonomic synonyms:
– Carya oliviformis (.. Michx f) Nutt.
– Carya pecan (Marsh.) Engl. & Graebn.
– Hicoria sin (Marsh.) Britton.
* See: Pecan in other languages
Family: Yuglandaceae
Origin: Native plant of the southernmost area OF United States (Iowa, Illinois, Indiana, Ohio, southern Alabama) and Mexico. It grows wild along the Mississippi River and its tributaries.
Archaeological remains date this tree in the State of Texas since time immemorial. For this reason and for its nutritional value, pecan is the official state tree of Texas since 1919. Formerly, its fruits were an important food for American Indians when food was scarce.
Habitat: Pecan need moist soil, rich in nutrients. It grows in plains and river banks.
Distribution: Southern US (The US is the largest producer of pecans, reaching 80% of world production)
Description of the plant
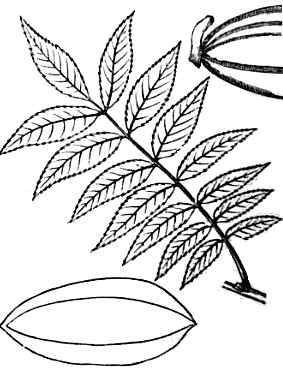 Illustration of a branch and a fruit of pecan |
Pecan (Carya illionensis) is a deciduous tree native to North America, measuring between 30 and up to 50m. high.
The gray trunk is branched into numerous ascending branches, forming a rounded crown.
Imparipinnate compound leaves, of 9-17 leaflets, narrow, acute apex and serrated margins. Limbo is yellowish green up and paler on the underside. Being a deciduous tree, it darkens and wilts in autumn.
The inflorescence is an axillary raceme, where flowers are arranged. These are monoecious, and the tree has male flowers and female flowers.
It blooms in spring, from April to May. Due to its high production of pollen, it is one of the main causes of hay fever in the United States.
The fruit is a brown nut, ovoid, 4-ribs, finished in tip and thin shell. They can measure up to 4cm. long, and occur in clusters from 3 to 11 nuts. The seeds ripen in October. It has a pleasant flavor and high nutritional value, mainly because of its fat content.
What parts of pecan are used?
- Fruits and leaves
- Wood
Uses of pecans
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Food: the fruits are used in food, raw or cooked. They are sweet and tasty, rich in fat and provide energy to the diet. The whole fruit is used for cakes, desserts, ice cream, candies and breads.
A vegetable milk is made from grinding pecan nuts, which is used as a thickener for soups and different preparations. The seeds are rich in fat and we can extract its oil, known as pecan oil. This oil is mainly used in cosmetics.
- Medicinal: Its fruit is of interest as a source of healthy fats, which benefit cardiovascular health and brain function. Also, because of its high energizing value, they are a nutritious food in cases of convalescence, weakness and fatigue.
From this tree leaves an astringent tea can be prepared. It can also be applied externally to combat parasites.
- Other uses: This tree wood is used as fuel and manufacturing of furniture.
Composition of pecans
- Fats: They are the main nutrient that pecan gives us, as it is an oily-rich nut. Among its composition, it is rich in fats of Omega 9 type (oleic acid) and linoleic acid (omega 6). It also provides linolenic acid (Omega 6.)
- Fiber: They are rich in insoluble fiber (10% of its composition), which provides satiety, prevents constipation and balances the high-fat food.
- Protein: The pecans are a good supply of good quality protein.
They contain essential amino acids like arginine, which has beneficial effects on the cardiovascular system. Also provides tryptophan and glutamic acid. The pecans are deficient in the amino acid lysine.
- Carbohydrates: It only contain 14% carbohydrates, like other nuts percentage.
It is low in carbohydrates, and these are mostly of slow absorption type (Complex carbohydrates). For this reason, it is a suitable food for low-carb diets, such as menopause or diabetes diet.
(* More info: Nuts benefits)
- Minerals: Pecans provide important minerals for bone health and the body in general, among which phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, manganese, selenium and zinc.
Compared to other nuts, Pecan is low in calcium (70mg. Calcium per 100g. Pecan, compared, for example, 264mg. Per 100g of almond).
However pecans are rich in trace elements such as boron, copper, chromium, nickel, rubidium, and vanadium.
- Vitamins: They are rich in pro-vitamin E, which protects and benefits the composition of body fat (the appearance of the skin, good cholesterol, etc.). Mainly contains provitamin as gamma-tocopherol.
It also provides vitamins from B group, which have energizing function in the body, such as inositol.
Nutritional composition of pecans per 100g. | |
Nutrient | Amount |
Calories (kcal.) | 691 |
Carbohydrates (g.) | 13,86 |
Proteins (g.) | 9,17 |
Fats (g.) | 71,97 |
Fiber (g.) | 9,60 |
Calcium (mg.) | 70 |
Magnesium (mg.) | 121 |
Phosphorus (mg.) | 277 |
Sodium (mg.) | 0 |
Potassium (mg.) | 410 |
Iron (mg.) | 2,53 |
Zinc (mg.) | 4,53 |
Copper (mg.) | 1,20 |
Manganese (mg.) | 4,50 |
Selenium (mcg.) | 6 |
Vitamin C (mg.) | 1,1 |
Vitamin B1 or thiamin (mg.) | 0,66 |
Vitamin B2 or riboflavin (mg.) | 0,13 |
Vitamin B3 or niacin (mg.) | 0,17 |
Vitamin B6 o pyridoxine (mg.) | 0,21 |
Folates (mcg.) | 22 |
Vitamin A (UI) | 77 |
Vitamin E (mg. ATE*) *alfa-tocopherol | 4,05 |
Water (g.) | 3,52 |
Other components
- Flavonoids: The plant is very rich catechins, a type of flavonoid with high antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
(More information)
Among its flavonoids, it contains: azaleatin, azaleatin-3-arabinoside, azaleatin-3-rutinoside.
- Heterosides: It also contains quercetin glucoside.
- Phytosterols: mainly beta-sitosterol. This is a plant component very similar to the animal cholesterol, that, in the intestine, it has the inhibitory effect of cholesterol absorption. A diet rich in phytosterols can help reduce the absorption of dietary cholesterol.
Botanical classification | |
Kingdom | Plantae – Plantas |
Subkingdom | Tracheobionta |
Superdivision | Spermatophyta |
Division | Magnoliophyta |
Class | Magnoliopsida |
Superorder | Rosanae |
Order | Fagales |
Family | Juglandaceae |
Gender | Carya |
Species | C. illinoinensis |
![]() More information on pecans.
More information on pecans.