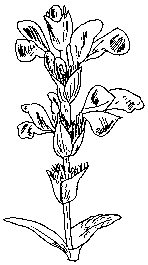Contents
Examples of parasitic plants
What are parasitic plants?
Most plants are autotrophic, which means they are able to make their own food, unlike animals. However, there are a few plants that are heterotrophic (They obtain their food from other plants), at least partially, such as the animals and other living things, including fungi, are.
Parasitic plants must be included among heterotrophic organisms. A parasitic plant is a plant that obtains the required nutrients, wholly o partially, from other plant.
Therefore, parasitic plants are plants that have adapted to live heterotrophically, either completely or partially. Adaptations of parasitic plants are based on the total or partial loss of chlorophyll as well as changes in the roots and other vegetative structures.
In the case of plants, parasitism is something rare, as it is only seen in some algae, as well as certain fungi. As superior plants, parasites specimens are only found within the group of angiosperms, except for the case of Parisitaxus usta, a gymnosperm conifer some authors consider that is not actually a parasitic species. Where there are more cases of parasitism between plants it is in the group of dicotyledons.
TYPES OF PARASITIC PLANTS
Parasitic plants are divided into 2 groups: Holoparasitic and hemiparasitic, depending on the degree of parasitism they present.
Holoparasitic plants

Broomrape (Orobanche sp) is a holoparasitic plant with a highly modified corm
In these parasitic plants parasitism is very clear, so there is a complete transformation of the vegetative plant apparatus (corm). For example, they do not have normal roots, but haustoria.
An haustorium or sucking holoparasitic plant root penetrates into the conducting vessels (xylem and phloem) of the parasitized plant.
This kind of plants do not have the typical greenish color, but rather pale or yellowish because they lack chlorophyll. They do not photosynthesize, so they are unable to synthesize organic substances, but the take them from the parasitized plant.
In some cases, the vegetative part of the holoparasitic plant is very small, altough these plants always have flowers to reproduce sexually.
Examples of holoparásitas plants, we cite the field dodder, (Cuscuta sp.) broomrape (Orobanche sp.) and Cytinus sp
Hemiparasitic plants
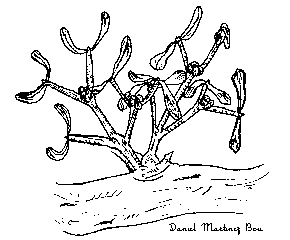
Drawing of mistletoe
The vegetative body of such plants (that is to say, roots, stem and leaves) is slightly transformed, but they all perform photosynthesis.
The hemiparasitic plants, as well as holoparasitic, have also transformed their roots into haustoria, although they are green because chlorophyll is present.
Hemiparasitic plants take nutrients, such as water and mineral salts, from xylem of plants they parasitize.
Mistletoe (Viscum sp) and Thesium sp are examples of hemiparasitic plants
Facts about parasitic plants
Cytinus parasitic plant, typical of the Mediterranean region, expels a smelly liquid from time to time that can produce terrible nausea and dizziness.
The “lucky plant” that is sold for Christmas having fruits like whitish balls is actually a parasitic plant native to the temperate and tropical regions of the world, called mistletoe (Viscum album)
Broomrapes have a certain host-parasite specificity. For example, Orobanche latisquama only parasitizes rosemary shrubs, rockroses (Estepa sp) and few more shrubs. Ivy broomrape only parasitizes ivy (Hederea helix).
Other plants with special nutrition
Within this group, in addition to the parasitic plants we have already seen, we include carnivorous and mycotrophic plants.
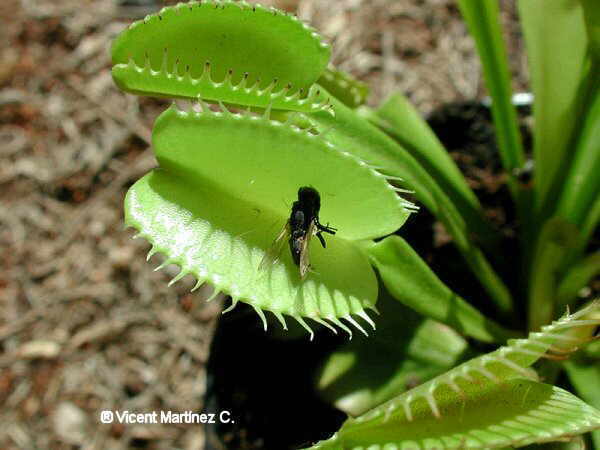

Flytrap photo. A carnivorous plant.
- Carnivorous plants: Carnivorous plants or insectivorous plants need to incorporate some essential components, such as nitrogen or phosphorus, through diet.
They do it with total or partial digestion of organisms (especially insects) that capture from the environtment.To do this, they have modified leaves and have active or passive mechanisms with which to capture their prey, mostly insects, but also small aquatic invertebrates in some cases. Carnivorous plants live in poor nitrogen environments and other plant nutrients.This type of plants performs photosynthesis
- Mycotrophic plants: These types of plants are in symbiosis with certain fungi. Plants obtain carbohydrates and other nutrients of the fungus. This symbiosis occurs between the root of the mycotrophic plants and the fungus in what it is known as mycorrhizae.
![]() More information on plants.
More information on plants.
16 November, 2020