Contents
What is an olive tree?
Characteristics of olive tree (Olea europaea)
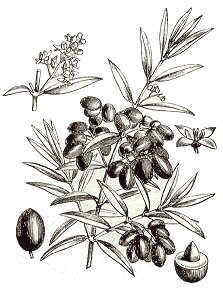 |
Common noun: Olive tree
Scientific noun: Olea europaea L.
Family: Olive family – Oleaceae
Habitat: The cultivated specimen can be found inside the area of Mediterranean influence of unirrigated lands. Wild olive tree (Olea europaea var. sylvestris) appears in dry places of Mediterranean climate.
Description of olive tree
Perennial tree of the Olive family – Oleaceae – up to 15 m.
Grayish stems when tree is young, darker as it grows. Bark desegregates into squared pieces.
Opposite leaves, till 8 cm., lanceolate, coriaceous, bright up, whitish below.
Fruits in drupe (Olive), edible.
The cultivated specimen can be found inside the area of Mediterranean influence of unirrigated lands. Wild olive tree (Olea europaea var. sylvestris) appears in dry places of Mediterranean climate.
Picking-up and storing: Leaves and bark can be collected throughout the year. Olives in autumn or winter. Leaves and bark must be dried and kept in a dry, well.- closed container..
Components of Olive tree
- Leaves: Glycoside oleouropein, tannins, dextrose,, hydrocarbons…
- Fruits: Oil (mainly formed by oleic acid – monounsaturated fat acid – and in less quantity by the acids linoleic palmitic…
Useful parts of Olive tree
The leaves, the fruits and the bark.
![]() More information on olive tree
More information on olive tree