Contents
Species of the genus “Quercus“
Different classes of oak trees
Among the approximately 600 species of the genus Quercus, they could be described as follows:

Downy oak (Quercus pubescens)
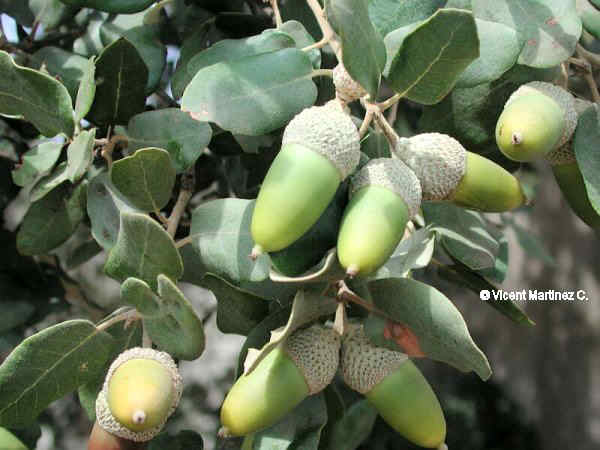
- Downy oak, pubescent oak (Quercus pubescens): Tree up to 15 m high, which can be found in Europe, Crimea and Turkey. The most abundant and pure populations are in the Pyrenees.
It is mainly characterized because the underside of the leaves is downy when young, ie has abundant hair,. Subsequently, usually leaving only those close to the nerves.
It has not too long fruits, with short stems, with half of the cup nut also pubescent. In the fall, the leaves turn ocher and remain on the tree throughout the winter (marcescent leaves) Its medicinal properties are similar to those of English oak.
- Gall Oak, Lusitanian Oak, Dyer’s Oak (Quercus lusitanica = Quercus faginea): Up to 20 meters high, a native of the Iberian Peninsula and North Africa. Adapted to withstand extreme conditions. It has small, bright green leaves on the top and pubescent on the underside. Its rather elongated fruits are used to feed livestock. It is used to treat vaginal warts and for the treatment of corns.
- Sessile oak (Quercus petraea = Quercus sessiflora): Central Europe and Southeast Europe that can measure 30 m. high. Has hardened leaves bright green on the top and pubescent on the underside with rounded lobes up to 15 cm. Up to 1500 m in the woods along with the English oak (Quercus robur) Widely used for the quality of its wood, used in herbal medicine to remove warts. From this species nutgalls are mainly obtained for the production of natural dyes
- French oak, English oak (Quercus robur): Up to 45 m in height. Erect stems with bark full of cracks and wrinkles, light gray in youth and darker as the tree gets older. leaves alternate, lobed, sessile, with rounded lobes and petioles very short, provided 2 atria to the larger base of the petiole up to about 12 cm. Fruit catkins, yellow-green. Acorns gathered in groups of 1-3 on the same stalk.
 Trunk of cork oak showing the cork
Trunk of cork oak showing the cork - Cork oak (Quercus suber): Natural from Iberian Peninsula. It is the tree whose bark cork is obtained from. It can reach 15 m high. It presents leaves much like evergreen oak, a little more narrow and elongated. They are dark above and whitish below because of its dense green hairiness. In phytotherapy, it can be used with properties similar to French oak.
- Sawtooth oak (Quercus acutissima): Tree growing in Japan, Korea and China, which can reach 15 m. Its long leaves, up to 15 cm, are very similar to those of chestnut. In herbal
medicine it is used as an astringent.
- White oak (Quercus alba): Tree from the United States and Canada that can reach 30 m. high. It has leaves up to 30 cm reaching purple hues in autumn. Its acorns are very small. It is one of the main trees for timber production in these countries, because it is very resistant to moisture and rot. It is used in herbal medicine as hemostatic, astringent, tonic and antiarthritic.
 Photo of holm oak (Quercus ilex). Leaves and fruits (acorns)
Photo of holm oak (Quercus ilex). Leaves and fruits (acorns) - Holm oak (Quercus ilex): Up to 20 m. erect stems gray. Elliptic leaves, bright green above, whitish below, up to 4 cm in length, with up to 11 pairs of lateral nerves. yellow flowers, gathered in hanging spikes. Fruit is a nut, (acorn) dark brown at maturity, bitter, inedible. Humid Mediterranean forests. In herbal medicine it can be used with properties similar to English oak.
- Holm oak (Quercus ilex subsp ilex = Quercus ilex rotundifolia subsp ballota..): up to 15 m. erect stems gray. pubescent elliptical leaves with whitish green above and gray below, up to 4 cm long, with up to 8 pairs of lateral veins. yellow flowers, gathered in hanging spikes. Fruit dark brown at maturity, edible. dry Mediterranean forests. In herbal medicine can be used with properties similar to English oak.
- Turkish oak, Austrian oak (Quercus cerris) from Southern Europe and Turkey. It is a tree that can reach 36 m high. It has narrow gray-green leaves with irregular lobes.. In herbal medicine used for the treatment of tumors.
- Kermes oak (Quercus coccifera): Evergreen shrub up to 2 meters. Stalks of a grayish color. Leaves entire or slightly toothed, dark green with a thorny margin. The young leaves have a lighter green and hairy beneath. The fruit is a nucule (acorn) more globular than the rest of Quercus and with scaly cup, ripening occurs in the second year. In scrubs and dry places. In herbal medicine used for the treatment of tumors.
- Japanese Chinquapin (Quercus cuspidata): Tree native to China and Japan up to 25 m in height. Fruita with a distinctive odor that are pollinated by flies. It is used for the treatment of ascites or perineal dropsy, is the accumulation of fluid in the lower abdomen as a result of certain diseases such as cirrhosis, heart problems, tumors, etc.
- Daimyo oak (Quercus dentata): Deciduous tree from eastern Asia (Korea, Japan and China) up to 15 m in height. abundant leaves, irregularly lobed up to 30 cm. In herbal medicine the bark and dust from its gills is used as an astringent.
- Red oak (Quercus falcata): Tree native to the southeastern United States that can reach 25 m high. The young buds are oxide red which gives it its name. Leaves up to 20 cm with very pronounced lobes and dense hairs on the underside. It lives in acid and poor soils. In herbal medicine it is used for the treatment of cancer.
- Texas live oak, plateau oak (Quercus fusiformis): Named for the elongated shape of acorns. It lives in Texas where it forms thickets. The leaves have a tooth at the apex and some lateral teeth and have a great pubescence on the underside. It is used in herbal medicine to treat coughs, asthma and as a tonic.
- Gambel oak, scrub oak, oak brush, Rocky mountains white oak (Quercus gambelii) is an evergreen shrub that can measure from 4 to 9 meters. It occupies the slopes of the Rocky Mountains above 1500 m above sea level, forming a dense thicket where acorns are a good food source for many animals. It is used for treating cancer.
- Bluejack oak, cinnamon oak, upland willow oak (Quercus incana = Quercus cinerea): shrub up to about 3 meters high that grows in dry areas of the southeastern United States. Its name derives from the bluegreen leaves. In herbal medicine is used as an astringent, as a diuretic and for the treatment of gonorrhea.
- Black oak, Eastern black oak (Quercus velutina): From the Eastern United States, it is quite cultivated in Europe. Its scientific name derives from the fact that it presents velvety buds. It is a tree that can reach 30 m high. dyes are extracted from its yellow inner bark. Its leaves are provided with pointed lobes can reach 30 cm in length. In herbal medicine it is used with properties similar to English oak.
Scientific list of Quercus species
| Quercus acerifoliaQuercus acuminata Quercus acuta Quercus acutissima Quercus aegilops macrolepis Quercus agrifolia Quercus alba Quercus aliena Quercus alnifolia Quercus annulata Quercus aquatica Quercus aquifolioides Quercus arizonica Quercus arkansana Quercus aucheri Quercus austrina Quercus ballota Quercus berberidifolia Quercus bicolor Quercus borealis Quercus boyntonii Quercus buckleyi Quercus bungeana Quercus californica Quercus calliprinos Quercus canbyi Quercus catesbaei Quercus cedrosensis Quercus cerris Quercus chapmannii Quercus chinensis Quercus chrysolepis Quercus coccifera Quercus coccinea Quercus conferta Quercus cornelius-mulleri Quercus crispula Quercus cualensis Quercus cuneata Quercus cuspidata Quercus daimio Quercus densiflora Quercus dentata Quercus depressa Quercus depressipes Quercus dilatata Quercus douglasii Quercus dumosa Quercus dumosa revoluta Quercus durata Quercus eduardii Quercus edulis Quercus ellipsoidalis Quercus emoryi Quercus engelmannii Quercus faginea Quercus falcata Quercus floribunda Quercus frainetto Quercus fruticosa Quercus fusiformis Quercus gambelii Quercus garryana Quercus geminata Quercus georgiana Quercus glabra Quercus glandulifera Quercus glauca Quercus graeca Quercus gravesii Quercus grisea Quercus havardii Quercus hinckleyi Quercus hindsii Quercus hintoniorum Quercus hirtifolia Quercus hispanica Quercus hondurensis Quercus humboldtii Quercus humilis Quercus hypoleucoides Quercus hypoxantha Quercus ilex Quercus ilex ballota Quercus ilicifolia Quercus iltisii Quercus imbricaria Quercus incana Quercus infectoria Quercus inopina | Quercus intricataQuercus ithaburensis macrolepis Quercus john-tuckeri Quercus kelloggii Quercus laceyi Quercus laevigata Quercus laevis Quercus lamellosa Quercus lanata Quercus lanuginosa Quercus laurifolia Quercus laurina Quercus leucotrichophora Quercus libani Quercus lineata Quercus lobata Quercus lyrata Quercus macranthera Quercus macrocarpa Quercus macrolepis Quercus marilandica Quercus michauxi Quercus michauxii Quercus minima Quercus minor Quercus mohriana Quercus mongolica Quercus montana Quercus muehlenbergii Quercus muhlenbergii Quercus myrsinaefolia Quercus myrtifolia Quercus nigra Quercus nutalli Quercus oblongifolia Quercus obtusiloba Quercus occidentalis Quercus oglethorpensis Quercus pachyphylla Quercus palmeri Quercus palustris Quercus parvula Quercus peduncularis Quercus pedunculata Quercus petraea Quercus phellos Quercus phillyreoides Quercus polymorpha Quercus pontica Quercus prinoides Quercus prinus Quercus pseudococcifera Quercus pubescens Quercus pumila Quercus pungens Quercus pyrenaica Quercus rhysophylla Quercus robur Quercus rotundifolia Quercus rubra Quercus rugosa Quercus sadleriana Quercus salicifolia Quercus sapotaefolia Quercus schneckii Quercus schumardii Quercus semecarpifolia Quercus serrata Quercus sessiliflora Quercus sessilis Quercus shumardii Quercus sonomensis Quercus stellata Quercus suber Quercus tardifolia Quercus texana Quercus tinctoria Quercus tomentella Quercus toumeyi Quercus trojana Quercus turbinella Quercus undulata Quercus utahensis Quercus vacciniifolia Quercus variabilis Quercus vaseyana Quercus velutina Quercus virginiana Quercus vulcanica Quercus wislizeni |
![]() More information on oak.
More information on oak.