Contents
What is a nettle plant
Characteristics of nettle
Common noun: Nettle, stinging nettle
Scientific noun: Urtica dioica L.
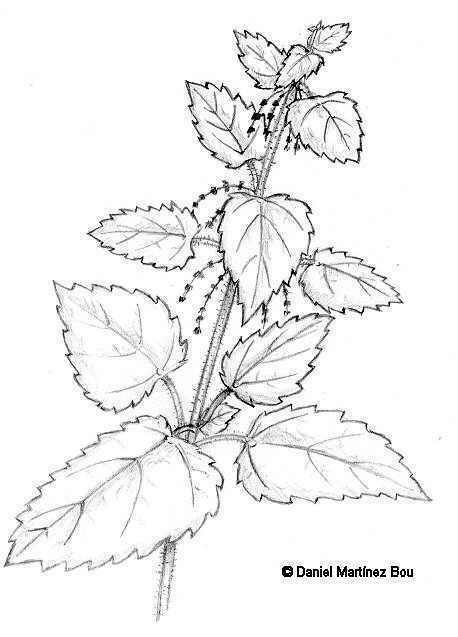 Nettle drawing Nettle drawing |
Family: Nettle family- Urticaceae
Habitat: In waste lands, rubbish dumps, by the side of the paths and in humid lands, with highly organic waste content
Description of nettle
Perennial plant of the nettle family – Urticaceae – up to 1,5 m. Square,erect stems. Leaves till 15 cm., serrated, pointed, dark green and covered, as the stem, by stinging hairs. Flowers in racemes, till 10 cm. long. Generally unisexual; female ones in long hanging catkins; male ones in shorter inflorescences.
Picking-up and storing nettles
Nettles can be collected at the beginning of spring till autumn. When used dried, they should be dried in the shade and stored in a a dry place

Roots must be collected at the end of august and, after being dried in the sun, they must be stored in an airtight container.
Components of nettle
– Acids: caffeic, ferulic, folacin (plant); linoleic, oleic and palmitic (seeds), formic, galic, acetic. (stinging hairs)
– Mucilage (plant)
– Lecithin (plant)
– Histamine (stinging hairs)
– Serotonin (stinging hairs)
– Acetyl-choline (stinging hairs)
– Tannins (plant, especially the root)
– Alcohols: glycerol (seed)
– Vitamins: vitamin B ( Niacin, riboflavin,thiamin, choline) (leaves); Vitamin C (leaves); beta carotene; vitamin K
– Minerals: Nitrogen, potassium, iron, calcium, sulphur, magnesium, aluminium (leaves)
![]() More information on nettles
More information on nettles








