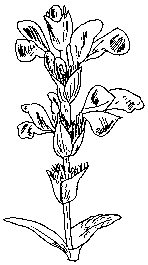Contents
What are mustard greens?
Characteristics of mustard greens
Common English name: Mustard greens, brown mustard, Indian mustard, Chinese mustard, leaf mustard, Kai Choi
Scientific name: Brassica juncea.
Taxonomic synonym: Brassica integrifolia (H. West) Rupr; Brassica japonica Thunb.; Brassica willdenowii Boiss.; Sinapis juncea L. : Brassica juncea var. juncea (L.) Czern.; Brassica juncea var. crispifolia L.H. Bailey; Brassica juncea var. japonica (Thunb.) L.H. Bailey; Brassica integrifolia (Vahl) O.E. Schulz
*See: Mustard greens in other languages
Family: Brassicaceae, or Cruciferae
Etymology: The term ‘mustard’ derives from the Latin “Mustum ardens”, which literally means “burning grape must”. This derives from an ancient preparation made with grape juice and mustard, that had a burning taste.
Botanical description of mustard greens
 Photo of mustard greens leaves
Photo of mustard greens leaves
Mustard greens (Brassica juncea) is an annual plant of the Brassicaceae family, between 30 and 100 centimeters tall.
Stem erect, smooth, branched and glaucous. Basal leaves pinnately divided, larger than the upper leaves, between 10 and 20 centimeters long, with toothed margins.
Upper leaves alternate, sessile or with short petiole, oval and lanceolate. Margins are mostly toothless. The inflorescence is terminal and erect.
Pedunculate flowers, yellow, formed by four crossed petals (characteristic form of Brassicaceae or cruciferous plants). The calyx consists of four equally crossed sepals. It contains six stamens. Indian mustard blooms from May to early October.
The fruit of the mustard plant is a nut in structure or dried leguminous silicua. This fruit is long, narrow and straight, thinner at the end forming a beak 4-5 mm and attached to the stem. Inside it. it contains the seeds, brown, with a size between 1.2 and 2 millimeters in diameter.
Used parts of mustard greens
- The leaves are cooked as a vegetable in African, Italian, Indian, Chinese and Japanese cuisines. It has a cabbage-like but more intense flavor.
- Mustard seeds for oil extraction. This oil is mainly used in India, and has a characteristic spicy flavor. Although it may seem unusual, the fact is that oil is also extracted from other cruciferous plants, such as rapeseed, perhaps the best known.
Composition of Mustard greens
- Protein
- Fat (higher content of the seeds in the leaves).
- Glycolipids (leaves)
- Fiber
- Isothiocyanates: Indian mustard seeds contain: the alilsevenol allyl isothiocyanate or isothiocyanate and crotonyl isothiocyanate.
- Minerals: calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, zinc
- Vitamins: Vitamin C, Vitamin A (as beta carotene)
- Oxalic acid (leaves): oxalates are components that prevent calcium absorption. This can be avoided boiling the leaves and discarding the cooking water. With this method, oxalates (which dissolve in water) pass to the cooking water and we reduce its intake.
| Composition of mustard greens (Brassica juncea) per 100g. | |
| Nutrient | Amount |
| Energy/ Calories | 26kcal. |
| Carbohydrates | 4,90g. |
| Proteins | 2,70g. |
| Fats | 0,20g. |
| Fiber | 3,30g. |
| Ash | 1,40g. |
| Calcium | 103mg. |
| Phosphorus | 43mg. |
| Magnesium | 32mg. |
| Iron | 1,46mg. |
| Sodium | 25mg. |
| Potassium | 354mg. |
| Zinc | 0,20mg. |
| Selenium | 0,90mcg. |
| Vitamin A | 5.300UI |
| Vitamin C | 70mg. |
| Thiamin (B1) | 0,08mg. |
| Riboflavin (B2) | 0,11mg. |
| Niacin (B3) | 0,80mg. |
![]() More information on mustard
More information on mustard