Contents
Whats is a moringa plant?
Characteristics of moringa (Moringa oleifera)
Common English name: Moringa, drumstick tree, horseradish tree, ben oil tree, benzoyl tree.
Etymology: The word “Moringa” comes from the Tamil word “Morungai” (= stick), because of the aspect of its young fruits. This word is used by most languages to designate this plant, with more or less variations. Thus, for example, in English, in addition to moringa is known as “drumstick tree”
Another form of popular designation is under the name of “ben” which refers to the name of the oil that is extracted from its seeds. For example: In German “behenbaun” or in English “ben oil tree”.
Other names refer to the shape of their flowers or leaves. Such is the case of “French jasmine” which is the name as it is popularly known in Colombia and Puerto Rico.
Common name in other languages:
 Illustration of this plant
Illustration of this plant
Scientific name: Moringa oleifera Lam.
The name of the genus “Moringa“, as we have seen previously, comes from the Tamil language “Morungai ருஙுங்கை”, “(= stick) by the form of its fruits.
“oleifera” is a Latin compound word formed by “oleum” (oil) and “ferre” (carry), therefore the name of the species means “containing oil”. This name refers to the oil that is extracted from its seeds.
“Lam” refers to Jean-Baptiste Lamarck (1774-1829) French naturalist who first names it in his book Encyclopédie Méthodique, Botanique(1785)
Synonyms: Guilandina moringa L.; Hyperanthera moringa (L.) Vahl; Moringa zeylanica Burmann; Moringa pterysgosperma Gaertn. Nom. Illeg.
Family: Moringaceae. It is a genus of 13 species of tropical or subtropical trees or herbs.
Origin of moringa: Native of the lands of southwest India, Pakistan and Afghanistan where it grows spontaneously at the foot of the Himalayan ridge.
Where does moringa grow?
 Detail of the leaves of moringa
Detail of the leaves of moringa
Habitat: From its place of origin it has spread to many regions of the world with tropical or subtropical climate (Arabia, tropical and subtropical Africa, Madagascar, Southeast Asia, Sri Lanka, Philippines, the Caribbean and Pacific islands and Latin America, Peru, Paraguay, Brazil, Puerto Rico…).
It is a tree that adapts very well to this type of climate, being able to live in places where rainfall is scarce due to its ability to adapt to aridity. At the same time, it is able to colonize a certain place to be a tree that presents a very fast growth.
How is moringa tree?
Deciduous tree of the family of Moringaceae, between 10 and 12 meters of height.
Stems erect, thick with a thick gray bark -white
Leaves composed, tripinnate between 30 and 60 cm in length, bright green.
Flowers of yellowish white color, about 2 cm in diameter with 5 petals and 5 sepals. They are gathered in hanging inflorescences. In places with seasonal differences, it blooms in spring.
In areas with no seasonal changes and constant rainfall, it can flower throughout the year or a couple of times a year.
Fruits in brown, dehiscent capsules (legumes) up to 45 cm in length. The fruits are mature from 3 months after the plant has bloomed.
Inside the fruits, there are dark brown seeds, with wings and very rich in oil, in number of 10 to 15.
Composition of moringa
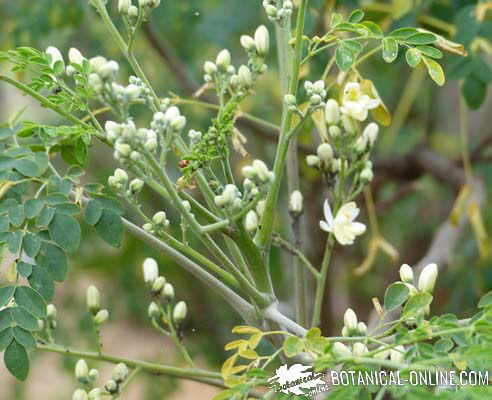 Moringa leaves and flowers
Moringa leaves and flowers
- Acids: Ascorbic (Leaves and fruits) caffeic (leaves) behenic, palmitic, stearic (seeds)
- Minerals: magnesium, sodium, phosphorus and potassium (shoots, fruits) iron (leaves, fruits and shoots) sulfur, calcium (leaves and fruits) copper,
- Amino acids:
* Essential Amino Acids: Phenylalanine, Isoleucine, Histidine, Leucine, Lysine, Methionine, Threonine, Tryptophan, Valine (shoots)
* Non-essential amino acids: aspartic acid (seeds), glutamic acid, alanine, arginine, cystine, glycine, serine, tyrosine,
- Vitamin B: Choline (leaves and fruits), niacin, thiamin (shoots, fruits), riboflavin (shoots, fruits and leaves)
- Vitamin E (Tocopherols in shoots)
- Fiber: (shoots, fruits, leaves, seeds)
- Oxalates: (leaves and fruits)
- Flavonoids: quercetin (fruits)
Uses of moringa
 Moringa seeds
Moringa seeds
Moringa is a tree from which numerous products are obtained. For example:
- Moringa seeds: Used mainly for the extraction of edible oil and for the production of biodiesel
- Leaves and flowers of moringa: They are edible and with them numerous dishes are elaborated. The flowers are very suitable for the bees to produce honey (Melliferous plant)
- Moringa pods and seeds: Used in the decontamination of water. They are an affordable, inexpensive and biodegradable way to purify water.
- Moringa wood: For firewood or charcoal for fire. For the production of cellulose with which a quality paper is obtained. For the textile industry.
- Organic fertilizer with moringa leaves: The leaves of this tree, when decomposed, produce a fertilizer of excellent quality, while having fungicidal properties, very suitable to eliminate or prevent fungi that can affect the roots of plants.
- Branches and leaves as fodder: The thinner branches and leaves provide food for goats, cows, camels and sheep.
- Moringa bark: Used to make paper, ropes, mats
- In gardening: As a garden tree or to elaborate hedges.
Moringa as a healing tree
In addition to food, industrial, home or agricultural uses, moringa is a tree that has been used since ancient times as a healing plant with varied properties. In India, its traditional uses point to it as antihypertensive, antidiabetic, antidiarrheal, antiansolytic, antigonorrhoidal, etc.
* More information about moringa medicinal properties
Moringa plant has been subjected to numerous medical studies
Based on its traditional uses, numerous medical studies have been carried out on animals to verify the efficacy of the traditional uses of this plant.
![]() More information on moringa.
More information on moringa.