Contents
What is a chamomile plant?
Characteristics of chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla)
Common name: Chamomile
Scientific name: Matricaria chamomilla L.
Family: Daisy family – Asteraceae/ Compositae
Habitat: In cultivated soils, sandy and uncultivated lands.
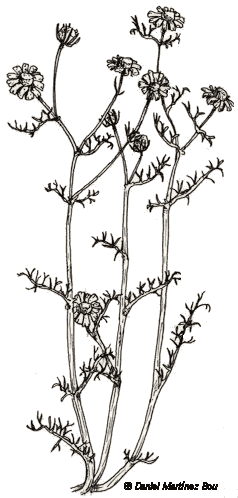
Botanical illustration of chamomile by ©Dibujosparapintar |
Description of chamomile
Annual scented herb of the daisy family – compositae – till 60 cm tall.
Erect glabrous stems.
Divided leaves, toothed- lobed.
Head flowers till 2,5 cm wide; White ligules, hanging as they grow up. Yellow florets, pentalobulated in a conical receptacle.
Picking-up and storing chamomile
The flowers should be harvested from spring to the first third of summer. They will have to be dried in the shade and to be stored in a closed and dark place, only during a year at the most.
- More information: How to collect and dry chamomile
Composition of chamomile
- Fructose, galactose (ground), glucose (flower)
- Mucilage
- Fatty acids: linoleic, palmitic, oleic.
- Vitamin C, beta carotene, choline
- Salicylic, caffeic, gentisic and pectic acid.
- Essential oil (0.2 to 2%): Azulene, alpha-bisabolol (50%), chamazulene (1-15%), farnesene, cadinene, furfural, matricarina, matricine, sesquiterpenes.
- Antemic acid (it is a bitter principle that can be emetic), farnesol, geraniol, borneol (plant), luteolin, apigenin, quercetin (yellow pigments), rutin, Coumarins (umbelliferone)
![]() More information on chamomile
More information on chamomile