Contents
What is a lemon balm plant?
Characteristics of lemon balm (Melissa officinalis)
Common English Name: lemon balm, balm, balm mint
Scientific name: Melissa officinalis L. The name “Melissa” comes from the distinct lemon smell that their leaves produce.

Family. Mint family (Labiatae)
Habitat. Where does lemon balm grow?
Natural from southern and central Europe. It grows wild in forests or along weeds in gardens, in organic-rich soils, in shady places.
It can be grown in many home gardens a as a medicinal plant and for pharmaceutical or cosmetic industry.
Description of lemon balm
Perennial plant of the Labiatae family of up to 80 cm tall.
Stems erect, square, woody.
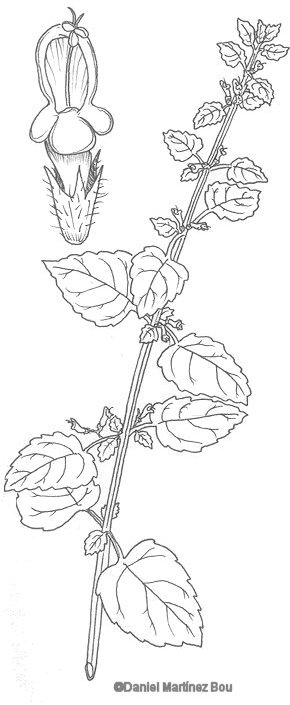
Leaves with very sharp teeth, with characteristic smell of lemon, stalked, oval.
White or pink flowers to 1.2 cm in diameter, gathered in whorls of up to 10 flowers. Chalice with many hairs. Bilabiate corolla; lower lips divided into 3 main lobes being the most prominent.
Lemon balm main components
- Essential oils: Melissa belongs to the mint family, like many aromatic herbs (thyme, rosemary, mint, lavender, etc.). All of them have in common a high content of essential oils, which are what give them the characteristic aroma of these plants.
Essential oils are also responsible for some of their properties. The entire lemon balm plant is rich in essential oils (0.4%), mainly: Thymol, citronellal, geranial, neral, limonene, etc.
- Flavonoids: Catechins, luteolin, quercetin, apigenin, camferol, tannins,
- Polyphenols: caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid , rosmarinic acid, oleanolic acid
- Acids: succinic, ursolic (plant), citronelic (buds).
- Beta-sitosterol
*More information: Properties of lemon balm
![]() More information on lemon balm
More information on lemon balm








