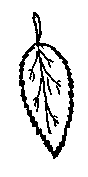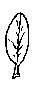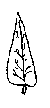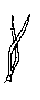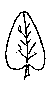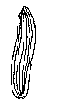Contents
Classification of a leaf
According to the petiole
Petiolated (Stalked) |
Sessile. (Unstalked) |
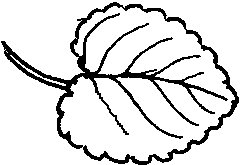
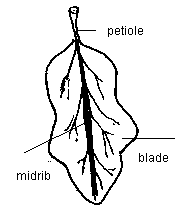
Petiolated leaves are those that have a petiole. This can be different in length from one plant to another.
Sessile leaves do not possess a petiole. The blade expands itself directly from the stem.
According to the blade
|
|
Simple leaves show an undivided blade or, in case it has divisions, they do not reach the midrib.
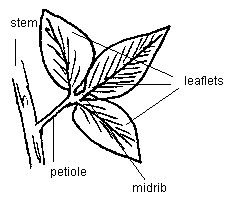
Compound leaves have a fragmented blade, with divisions reaching the midrib. Sometimes each one of these fragments is similar to a single leaf. They are called leaflets.
According to the edge
|
|
|
| Lobed
|
Entire leaves have a smooth margin.
Sinuate leaves have little curves with smooth edges like waves.
Dentate leaves have little teeth at the margin.
Serrate leaves have little bent teeth like those of a saw.
Lobed leaves have divisions that do not arrive the center of half blade.
According to the shape of the blade
|
|
|
|
| |
| Hastate | ||
|
|
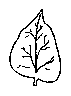
Elliptic leaves: remembering to a ellipse. 2 or 3 times longer than wide
Lanceolate leaves: spear-shaped. Gradually extending at the base and lessening to the apex.
Acicular leaves: needle-shaped. Several times longer than wide; ending sharply at the apex.
Ovate leaves: egg-shaped. Wider at the base than the apex.
Cordate leaves: heart-shaped. More extended at the base than the ovate type and with a notch
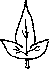
Hastate leaves: halberd-shaped. Remembering to that old fashioned weapon which was a combination between a spear and a battle-ax. Wider at the base but with lobes ending sharply.
linear leaves: strip-shaped. Several times longer than wide. Not pointed at the apex like in the acicular type.
According to the veins
|
|
|
Parallel-veined leaves: the veins run at the same distance to each other, like in canes.
Pinnate leaves: There is a main nerve, called midrib, from which the other nerves derive, remembering a plume.
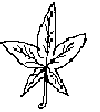
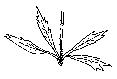
Palmate leaves: The nerves diverge from the main point such as the fingers do in the palm of the hand.
According to the arrangement along the stem
|
|
|
|
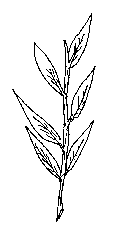
alternate: springing one per node at different levels of the stem.
opposite: two per node, facing opposite sides of the stem.
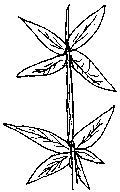
whorled: Several leaves disposed at the same level around the stem.
rosulate forming a rosette, like a ring around the stem.
| Do the following activities before the test: | ||
| Activity 9 | Activity 10 | Activity 11 |
Now you can do the test: | ||

Examination on leaves for primary school children.
Observe the following plants and choose the suitable answer in each case:
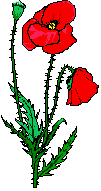
How would you define the poppy leaves according to the margin?
Lobed
Dentate
Sinuate

How would you define the mint leaves according to the nerves?
Palmate
Parallel-veined
Pinnate
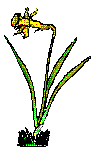
How would you define the daffodil leaves according their arrangement along the stem?
Whorled
Opposite
Rosulate
 Go back to main page “The leaves”
Go back to main page “The leaves”
To know more about “The leaves”
![]() More information about plants.
More information about plants.