Contents
What is an ivy plant?
Characteristics of ivy (Hedera helix)
Common English Name: Ivy, English ivy, European ivy, woodbind.

Scientific name: Hedera helix L.
– Etymology: The name of the genus “Hedera” comes from the Latin haerere (= to take hold) and it is due to its ability to climb on other plants clinging with its aerial roots.
– Synonym: Hedera canariensis Willd. = Hedera poetarum Bertol = Hedera poetica Salisb.
– Family: Araliaceous (Araliaceae)
Habitat: where to find ivy plants?
Europe, North Africa and Asia. We can find it from the south of Scandinavia to the Iberian Peninsula, reaching by the east Cyprus and the north of Turkey.
It grows mainly in shady places in forests, walls, rocks, etc., From sea level to about 1000 m altitude.
It has been introduced in many places in the rest of the world. Its ability to adapt to different types of terrain and climates has determined that, in many of them, it has become an invasive plant.
Such is the case in the United States and Australia where its cultivation is discouraged and information leaflets are provided explaining how to eradicate it.
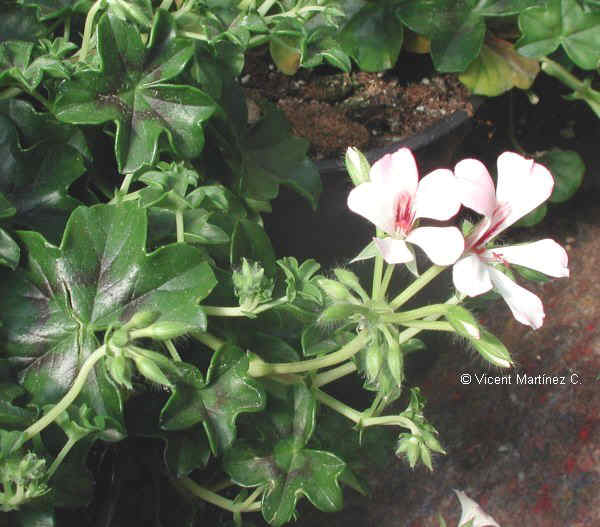
Description of ivy

Perennial climbing shrub of the Araliaceae family up to 30 m. Adventitious roots that allow it to cling to walls or other supports and climb.
Leaves between 5 and 10 cm in length; Dark green bright above; light green on the underside; Alternate, petiolated and with evident innervation. The younger, palmately-lobulated with 3-5 lobes; The adults or those that are exposed to the sun, whole.
Yellowish green flowers 3 to 5 centimeters in diameter, arranged in clusters composed of numerous umbels. They have 5 stamens and five petals.
Fruits in berry, purple or yellow black, according to the different subspecies. Flowering occurs from late summer to early fall. The fruits develop throughout the autumn and winter and mature in spring.
Main Components of Ivy
- Saponins: Hederin (Fruits and leaves) Bamirin, hederagenin, hederacoside (Fruits).
- Acids: chlorogenic acid, formic, malic, caffeic acid
- Rutin
- Quercetin
- Unidentified estrogen hormones (Leaves)
![]() More information on ivy plant
More information on ivy plant