Contents
What is a horsetail plant?
Equisetum arvense characteristics
Common noun: Horsetail, Bottle-brush, Shave-grass.
Scientific noun: Equisetum arvense L.
Family: Equisateaceae
Habitat: By the rivers. streams, borders of humid walls.
Characteristics of horsetail
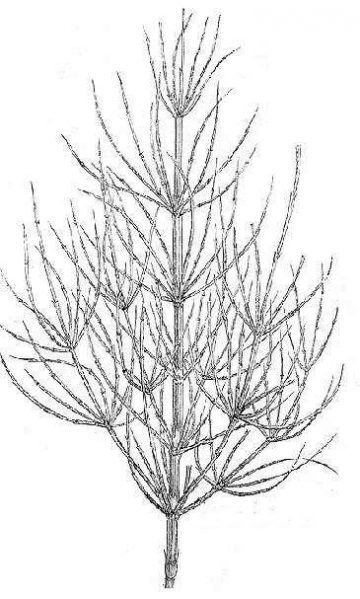
They are very primitive plants that were related with ferns. About 50 species are known worldwide, most of them in the North hemisphere.
Picking-up and storing horsetail
Only sterile stems possess medicinal properties. They will be picked up during summer and, after drying them in the sun, they will be kept in some dry and clean hermetic recipient.
Botanical description of horsetail
Perennial rhizomatous plant of the Equisateceae family up to 60 cm. Pale brown, erect stems, hard and hollow, very rough to the touch, starting from very vigorous rhizomes. They appear before the fertile stems.
Fertile stems up to 30 cm, finished in a head (strobils) bearing the esporangiums, where from spores are dispersed.
Sterile stems higher than fertile ones, grooved, with very characteristic leaves (microphylls) that group in the verticils and whose borders are united one to the others.
Thinner stems that arise from the verticils and formed by a succession of appendixes becoming thinner progressively.
Composition: Active components of horsetail
- Acids: ascorbic, ferulic, silicilic, malic, caffeic, gallic, pectic, tannic (Plant)
- Campesterol (Plant)
- Equisetrin (Plant)
- Equisetonin (Plant)
- Alkaloids: nicotine, palustrine. (Plant)
- Amino acids: Niacin (Plant)
- Fiber (plant)
- Minerals: Magnesium, silicon, silica selenium, calcium, iron, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, aluminum, zinc, chrome, cobalt (Plant)
![]() More information on plants
More information on plants








