Contents
What is a fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum)?
Characteristics of fenugreek
Common English name: Fenugreek, bird ‘s foot, Fresh Menthi, Greek -clover, Greek Hay, Sicklefruit, Cooper’s Clover
Etymology: Fenugreek is derived from foenum- graecum, which in turn gives the scientific name of this plant. Foenum – graecum means ” Greek hay “. It was named line this because of the strong smell of this plant, reminiscent of the hay, as intensively cultivated in the Mediterranean region.
Note: Fenugreek can also refer to common names that alfalfa plant (Medicago sativa) is given.
Botanical name: Trigonella foenum – graecum L.
Taxonomic synonym: Foenugraecum sativum Medik; Foenugraecum officinale Moench; Buceras odoratissima Medik ; Telis foenum – graecum.
Family: Fabaceae or Leguminosae. Subfamily: Papilionaceae
Origin: Western Mediterranean native plant and spread throughout the Mediterranean region since ancient times.
Habitat: roadsides, uncultivated land, dry grassland, wasteland and harvesting lands (grain fields).
Geographical Distribution: Middle East, Persia, India, China, Central and Southern Europe, Mediterranean region, North Africa, United States.
Description of Fenugreek
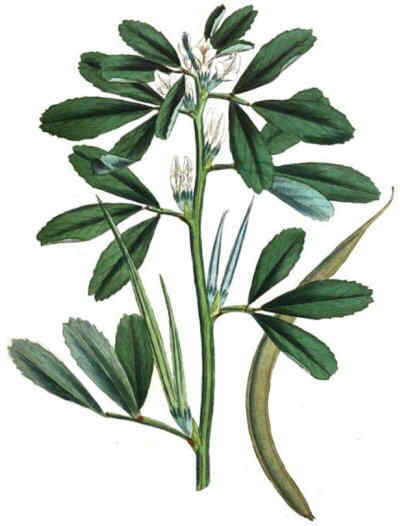
A drawing of the plant
Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum – graecum) is an annual herbaceous plant of the Leguminosae family, measuring between 20 and 50cm (up to 100cm.) high.
Stem erect, branched, grooved and with little pubescence.
The leaves are compound, petiolated, consisting of three oblon gleaflets, attenuated towards the base and with toothed margins. Size 20-50 x 8 -17mm.
The flowers are white or yellow, grow from the leaf axils and are arranged singly or in little groups of twos. Corolla 12 – 18mm. It flowers in April and May.
The fruits are pods or legumes narrow and oblong, resembling a sickle. Pod 80-150 x 2 – 4mm., With elongated beak at the end. The fruits ripen in summer and harvested in autumn.
Inside of them, there are between 10 and 20 tiny seeds, 3mm. approximately yellow, quadrangular and with a groove in the central part.
The whole plant gives off an unpleasant odor, reminiscent of hay.
Used parts
- Seeds: small grains are used as a condiment or spice, and in herbal medicine for its medicinal properties. These seeds have an unpleasant taste, so that they are used in small quantities or mixed with other aromatics, such as curry mix. Fenugreek meal is used in the food industry for its thickening capacity as a soluble fiber (up to 15% is galactomannan) and as a flavoring because ofr the essential oil components.
- Leaves: The leaves of this plant are edible, such as alfalfa (Medicago sativa). In some oriental restaurants, they are consumed in the traditional alu methi, made with steamed fenugreek leaves. This delicacy, little known in the West, is a vegetable particularly rich in choline and betacarotene.
- Grass pasture: Fenugreek is also a fodder plant. Like other pasture legumes, fenugreek increases the production of milk and meat of cattle. It also improves reproduction of flocks and it is a major source of digestible protein of good quality.
* More information: Fenugreek uses
| Composition of grains or fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum)per 100g. | |
| Nutrient | Amount |
| Energy/ Calories | 323kcal. |
| Carbohydrates | 58,35g. |
| Proteins | 23g. |
| Fats | 6,41g. |
| Fibra | 24,60g. |
| Vitamin C | 3mg. |
| Thiamin | 0,32mg. |
| Riboflavin | 0,37mg. |
| Niacin | 1,64mg. |
| Iron | 33,53mg. |
| Calcium | 176mg. |
| Phosphorus | 296mg. |
| Magnesium | 191mg. |
| Potassium | 770mg. |
| Sodium | 67mg. |
| Selenium | 6,30mcg. |
| Fenugreek medicinal c omponentsin parts per million (ppm.) | |
| Diosgenin | 19.000ppm. |
| Trigonelline | 1.300ppm. |
| 4-hydroxyisoleucine acid | 900ppm. |
| Choline | 500ppm. |
| Fenugreekine | 267ppm. |
| Gitogenin | 100ppm. |
| Nicotinic acid | 35ppm. |
Composition of Fenugreek
- Carbohydrates: fructose, sucrose, xylose, arabinose, raffinose, stachyose, verbascose
- Fiber: It has a high percentage of soluble fiber, such as mucilage and galactomannans. This type of fiber, which accounts for 2545% of the whole grain, provides emollient effect, protects the digestive mucosa and it is a natural intestinal regulator. It also has soluble fiber (lignin).
- Protein: fenugreek is high in easily assimilated protein and rich in phosphorus, so it has been indicated as a plant tonic. It contains mucins, which are a type of protein with gelling power.
- Aminoacids: cysteine, proline, tryptophan, phenylalanine and lysine. It also contains 4hydroxyisoleucine acid with cholesterollowering properties.
- Fat: It contains lecithin. Among its fatty acids, predominates linoleic acid.
- Minerals: calcium, phosphorus, potassium, selenium, chromium, copper, sodium.
- Choline, xanthophyll.
- It contains trigonelline (0.20.3%) (nicotinic acid derivative) and trigonellosides. This substance has hypoglycemic action.
- Steroid saponins, derived from furostane, (0.61.7%) have therapeutic effect for treating the symptoms of menopause. Also diosgenin, yamogenin, gitogenin, dioscin, graecunins, tigogenin, neotigogenin. Also contains fenugrecin (fenugreekine) 3peptide ester derivative of diosgenin. All these components are the bitter principle of fenugreek essential oil.
- Aromas: The aroma of fenugreek is also due to a glactone called sotolone (3hydroxy4,5dimethyl2 (5H)furanone)
- Cglycosides flavonoids: vitexin, isovitexina, orientin, homoorientina, vicenina1, vicenina2.
- Phytosterols: betasitosterol.
- Phenolic compounds: coumarins and flavonoids (quercetin, luteolin, rutin, kaempferol).
- Alkaloids: carpaine, gentianine
![]() More information on fenugreek.
More information on fenugreek.