Pea family plants characteristics

Photo of Spartium junceum L.
The pea family –Fabaceae, Leguminosae or Papilionaceae– has about 19.400 species of plants growing mainly in the temperate regions.
The most common species are herbs, but some of them are shrubs and trees, too.
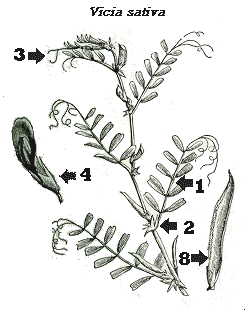
| Leaves (1): composite, seldom single, with very conspicuous stipules. (2) in many cases ending in tendrils or filaments (3). Sometimes leaves are reduced to spines. |
|
| Flowers: | |
| In racemes. | |
| Calyx (4): 5 joined sepals. | |
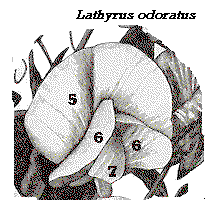
| Corolla: 5 petals. One at the top, called standard (5); two sided ones, called wings (6) and two joined ones below which form the keel (7) |
|
| Stamens: 10 usually joined into a tube. | |
| Style: 1 | |
| Ovary: superior | |
| Fruit: Pod (8) dehiscent into two valves. |
Genera
They are about 450 genera. The most important ones are the following:
| ACACIA ADENOCARPUS ANAGYRIS ANTHYLLIS ASTRAGALUS CALITOME CERCIS CHAMAECYTISUS CHAMAESPARTIUM CICER COLUTEA DORYCNIUM | ERINACEA GALEGA GLYCYRRHIZA HIPPOCREPIS LATHYRUS LOTONONIS LOTUS LUPINUS MEDICAGO OXYTROPIS | PHASEOLUS PSORALEA ROBINIA ROBINIA SCORPIURUS SAROTHAMNUS TELINE TETRAGONOLOBUS TRIGONELLA TRIGONELLA (Vicia cracca subsp. incana) |
![]() More information on plants
More information on plants