Contents
What is an European loquat tree?
Characteristics of medlar (Mespilus germanica)
Common name: European medlar, common medlar or medlar
– Spanish / Español: Nisperero europeo, nisperero común
Note: there are two species of loquats. The most popular is the Japanese loquat, which is the species Eriobotrya japonica. There is also the European loquat, common medlar or European medlar, which is explained in this botanical sheet.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Description of European loquat
European loquat or European medlar (Mespilus germanica) is a deciduous tree that is used as ornamentals for its attractive foliage, along with cultivated for the production of fruit. In Spanish, it is called nisperero europeo.
This fruit tree belongs to the Rosaceae family, being related to apple, hawthorn and blackthorn.
Long-lived, slow-growing tree, measuring between 7 and 8 m. high and 4 m. wide.
Robust trunk, grayish brown bark, sometimes with thorns. The trunk branches at the crown, which is conical in shape. The branches are hairy when young.
Leaves large, short stalked, long elliptical and dull green; with gray tomentose underside. Serrated margins. It is used in ornamentation for its showy leaves, which turn orange and yellow in autumn.
Flowers are large, 3-5cm. in diameter, solitary, white. They are white or yellow in color, without a peduncle, and their sepals stand out, which are visibly longer than the petals.
Hermaphrodite flowers that are pollinated by insects. This tree attracts many garden fauna: bees, meliponids, butterflies, flies, wasps and ants.
It blooms in the second half of May.
The fruits are drupes, also known as loquats. They are between 1 and 3 cm in size. in diameter, globular or pyriform in shape, with hairiness. Persistent sepals in the fruit.
The fruits do not always ripen when grown in cold areas. It is harvested in late autumn, and can be preserved for a long time, with the stems facing up, until the point of ripening in which the pulp acquires a brownish color and a very sweet flavor.
Inside the fruit, there are 5 hard seeds, elongated and brown.
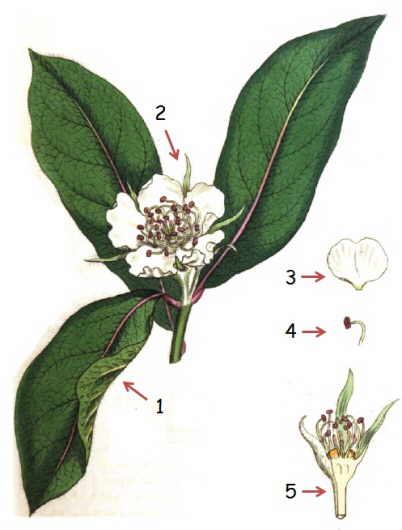
Pictured: illustration of European loquat
Marked: (1) leaf; (2) flower; (3) petal
(4) stamen with anther or pollen sac
(5) flower cross section
Used parts
- Fruits: The fruits are edible and have a pleasant flavor when ripe. Currently this species has been displaced from the markets by the Japanese loquat (Eriobotrya japonica). It has medicinal properties.
*More information: see Medicinal properties of the loquat in the following list.
- Bark: It can be a substitute for quinine, although it is not used. The wood is hard and flexible.
- Seeds: They are toxic due to their hydrocyanic acid content.

![]() More information on loquats
More information on loquats








