Contents
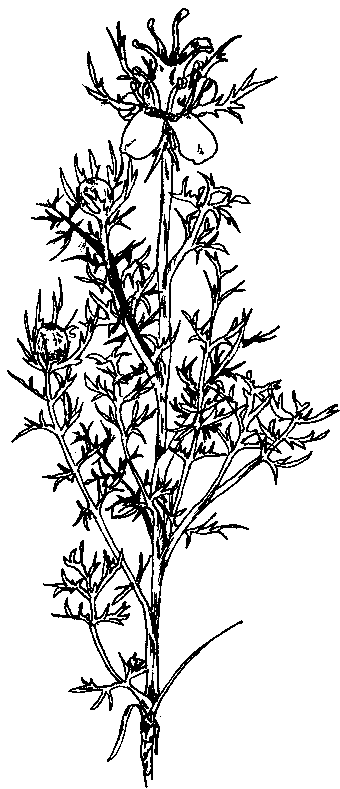
What is an echinacea plant?
Scientific and common noun of the main used species of gender Echinacea

Echinacea angustifolia: Narrow-leaved purple coneflower. North American species found in United States and Canada
Echinacea purpurea: Eastern purple coneflower, hedgehog coneflower, purple coneflower. North American species that grows in Eastern United States and Canada.
Echinacea pallida: Pale purple coneflower. United States
* See: Echinacea in other languages
Family: Daisy family. (Asteraceae or Compositae)
Habitat: Where to find these plants?
They grow wild in United States and Canada in grasslands, sandy soils and hills, but they can be found cultivated as garden plants in many regions.
Echinacea description
The genus Echinacea contains a number of plants in the daisy family very similar to daisies. They are noted for their large flowers with very long ligules and a large disc floret, sometimes thorny. Although there are nine species in this genus, the three mentioned above are the most commonly used as medicinal plants, being Echinacea angustifolia in Europe and Echinacea purpurea in America those that have a more general use.
Components of Echinacea

- Acids: ascorbic (seeds) butyric acid, ferulic acid, chlorogenic acid (plant) p-coumaric, syringic, caffeic, salicylic acid (leaves)
- Alkylamides: Echinacea (Echinacea purpurea and Echinacea angustifolia) contains at least 20 alkylamides.
- Polysaccharides: Sugar, starch, pectin (root)
- Paraffin wax (plant)
- Betaine (1%) (root)
- Alkaloids: (0.007%): Type pyrrolizidines such as tussilagine are found in very low concentrations (root)
- Flavonoids: Apigenin, camferol, luteolin, rutin, rutoside
- Amino acids: asparagine = altheine (root)
- Fiber: Inulin (root), mucilage (root and leaves)
- Starch (root)
- Tannins (root)
- Lecithin (root)
- Vitamins: B group vitamins: Riboflavin, niacin, thiamin (root), beta-carotene (root) and vitamin C (root)
- Minerals: aluminum, calcium, cobalt, chromium, iron, magnesium, silicon, sodium (root)
- Alcohols: Faradiol, taraxasterol, Arnidiol, beta-sitosterol (Flower)
- Essential oil: rich in thymol
![]() More information on echinacea
More information on echinacea