Contents
What is a turmeric?
Characteristics of turmeric (Curcuma longa)

Turmeric flowers and leaves
Common English Name: Turmeric, Indian saffron…
Scientific name: Curcuma longa L. The name derives from ” kurkum” that in Persia meant saffron.
Taxonomic synonyms: Curcuma domestica Valeton., Amomum curcuma Jacq.; Stissera curcuma Raeusch., Curcuma zedoaria Berg.; Curcuma aromatica Salisb.
*See: Turmeric in other languages
Family: Zingiberaceae
Where is turmeric from?
Originally from South-East Asia, it is cultivated in pan-tropical areas.
It grows in arid geographic areas with substantial rainfall to develop its rhizomes, which are intended for culinary use.
In Asian countries it is a common grass, and in some areas it has become a “weed” field.
Botanical description of turmeric
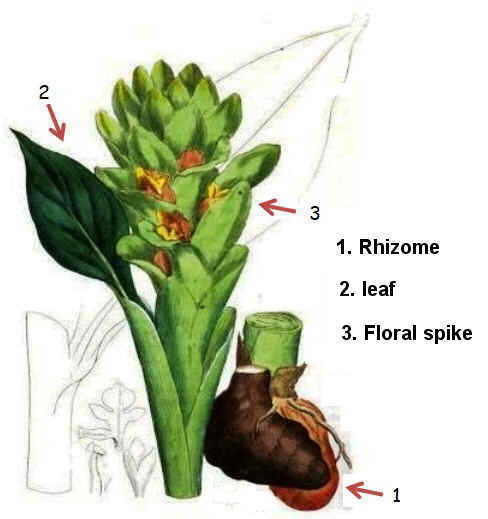
Turmeric is a perennial plant from 60 centimeters to 1.5 meters high. It has thickened rhizomes, finger-shaped, that is to say, underground stems with several buds, and grows horizontally.
From rhizome roots and herbaceous plant shoots arise. Rhizome supports the plant because it is rich in starch, so it is also the part that is consumed in the kitchen. It can remind us the ginger rhizome, cylindrical in shape, color and with a distinctive bright orange or yellow inside. Its surface is gray, brownish or yellowish color.
It is a stemless plant, that is, it has no stem and leaves arise directly outside from rhizome
The Latin name of the plant, Curcuma longa, refers to the leaves with long petioles, oblong limbo, large and thin. Measuring 20 to 70 centimeters long and 8-18 cm wide, although some somples can reach sizes up to 1.2 meters.
Its inflorescence is terminal, spike- shaped and cylindrical, bearing spikes up to 20cm long. They have laterally green united bracts with reddish spots.
Its flowers are zygomorphic, hermaphrodite and bracteate. The calyx is tubular, with three sepals and a crown made up of three petals, yellow or white.
Composition of turmeric
- Starch: the rhizome contains ukonan A (mainly), B, C and D, a type of polysaccharide with immune activity. It contains arabinose, glucose and fructose.
- Fats, protein, fiber.
- Vitamins: Vitamin C, beta carotene.
- Minerals: calcium, manganese, selenium, chromium, copper, cobalt, boron.
- Anthraquinones: 2hydroxymethylanthraquinone.
- Monoterpenes: 1,8cineole, camphene, terpinene, azulene, alphaphellandrene, borneol, camphor, alphapinene, 2bornanol, sabinene
- Sesquiterpenes: alantone, turmerone, bisacumol, bisacurone, bisabolene, caryophyllene, curcumene, curcumenone, bisabolene, betasesquiphellandrene
- Steroids: campesterol, stigmasterol.
- Organic acids: caffeic acid, caprylic acid, cinnamic acid.
- Polyphenol: curcumin (chemically: 1,7bis (4hydroxy3methoxyphenol) 1,6heptadiene3,5dione) or dipheruloylquinone).
- Curcuminoids: bisdemethoxycurcumin, dihydrocurcumia, dehydroturmerone, curlone.
- Terpenes: curzerenone.
- Phenols: guaiacol.
Composition of turmeric rhizome per 100g. (Curcuma longa) | |
Nutrient | Content |
Calories (Kcal) | 354 |
Carbohydrates (g) | 64,93 |
Proteins (g) | 7,83 |
Fats (g) | 9,88 |
Fiber (g) | 21,10 |
Vitamin C (mg) | 25,90 |
Vitamin B3 or niacin (mg) | 5,14 |
Iron (mg) | 41,42 |
Zinc (mg) | 4,35 |
Selenium (mcg) | 4,50 |
Manganese (mg) | 7,83 |
Phytochemicals in turmeric essential oil (Curcuma longa) | |
Nutrient | Amount (in ppm) |
Curcumenene | 121.700 |
Curcumin | 38.888 |
Turmerone | 43.200 |
Cineole | 29.200 |
Terpinene | 27.200 |
Curcumenol | 21.300 |
Curzerenone | 20.400 |
Curdione | 11.900 |
Desmethoxycurcumin | 11.100 |
Limonene | 2.300 |
Eugenol | 2.100 |
Linalol | 1.600 |
D-camphor | 1.500 |
Alpha-phelandrene | 720 |
Terpineol | 500 |
D-camphene | 480 |
D-sabinene | 432 |
Isoborneol | 200 |
Dihydrocurcumin | 57 |
![]() More information about turmeric.
More information about turmeric.








