Contents
What are courgettes?
Courgettes are the fruits of a variety of gourd belonging to the species Cucurbita pepo ssp. pepo.
Differences between a courgette and a squash
- A butternut squash, unlike other gourds, has a more bushy aspect, with several branches arising from a core, instead of the characteristic creeping form of most of the gourds.
- Courgettes generally have cylindrical shape although there are other varieties which are more rounded.
- They may have different colors, from light green to darker green.
- The leaves of the plants producing zucchini are large and generally have more spots than the rest of the pumpkin plants.
Types of courgettes
There are basically two criteria to classify courgettes-producing plants:
- By the shape of the plant:
- Open pumpkin plant: plants have a loose look and a very dense bush. Within this class we would have varieties like Gold, Black zucchini or Caserta.
- Closed pumpkin plant: They produce a more dense and closed bushy form. Within these we could include varieties such as Mexican Globe or Black Eagle.
- By the color of the fruit:
- Greenish.
- Dark-greenish.
- Dark-greenish with lighter patches.
- Light green.
- Yellow.
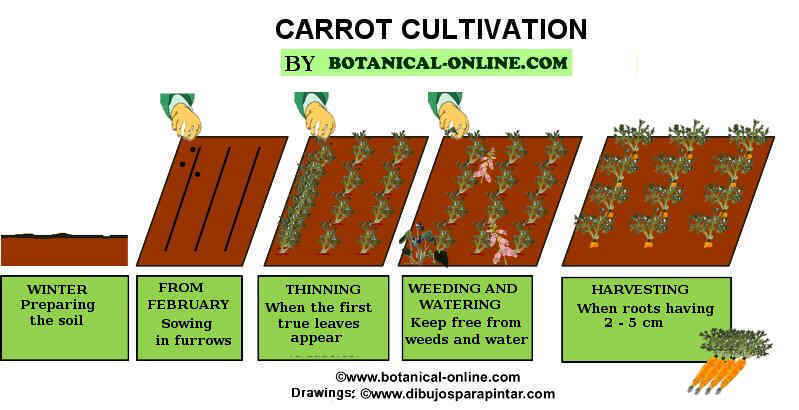
When to collect courgettes?
Courgettes are picked when they are tender. The majority can be eaten after a month or month and a half after planting the pumpkin. Between 15 and 20 cm is usually the most appropriate height to cut, although there are very tender varieties can be left to grow more.
However, it is a good measure not to let the courgettes become hard on the ground. Removing them from the plant is the best way to make the plant produce new tender fruit.
Courgettes should be eaten once collected since, in the absence of a hard crust, last very little and rot easily. Zucchini seeds are not suitable for planting since they have not matured yet and will not germinate.

Photo of courgette plant with some courgettes and flowers
Properties of the courgettes
Basically, courgettes food display similar properties to the rest of pumpkins. Being picked up very tender, its content in water is higher. They have fewer calories for its high percentage of water and the fact of having fewer carbohydrates, as their sugar content is lower since it is a poorly developed fruit.
However, their vitamin and mineral content is as high as in the rest of pumpkins, even surpasses many varieties in potassium and vitamin C content is higher in summer squash. All this, makes it very light food, ideal for weight-loss diet or eliminate body fluids. At the same time, its high mineral content makes it suitable for remineralizing the body.
Which are the best courgettes?
Courgettes with better flavor or texture are those who still have not grown much. Those called zucchinis are the most recommended dietetically speaking. They contain lots of vitamin C, a lot of vitamin A antioxidants ( beta carotenes) and more potassium than in summer squash. (To view in more detail the properties of pumpkins, go to the list below the chapter)
If a slighter variety is preferred, large zucchini, should be chosen, although it has fewer nutrients, water content is much higher and can help reduce weight. We must not forget that in this type of diet is best to eat zucchini boiled than to fry them so as to avoid ingesting more calories than necessary.

A detailed photo a a courgette with some flowers
From a culinary point of view, courgettes are not as usable as pumpkins and their use is often restricted to the manufacture of creams, fillings, salads or casseroles. The main countries that consume a lot of zucchini are Great Britain and Mexico.
Composition of courgettes
Composition of the pulp of the raw courgettes/ zucchinis by 100 gr. | |
95, 2 g | |
Calories | 15 kcal |
0.07 g | |
1.03 g | |
2, 90 g | |
1.2 g | |
248 mgs | |
32 mgs | |
0, 42 mgs | |
5 mgs | |
22 mgs | |
15 mgs | |
0, 057 mgs | |
0, 20 mgs | |
0, 127 mcg | |
9 mgs | |
340 UI | |
B1 vitamin (Thiamin) | 0.070 mgs |
B2 vitamin (Riboflavin) | 0, 030 mgs |
B3 vitamin (Niacin) | 0, 400 mgs |
B6 vitamin (Pyridoxine) | 0, 089 mgs |
0, 12 mgs | |
22 mcg | |
* Related information:
Medicinal properties of pumpkins
Pumpkin flowers / Pumpkin seeds
![]() More information on courgettes and pumpkins.
More information on courgettes and pumpkins.