Contents
What is chlorophyll?
Definition of chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is a basic component of plants and algae since it is the green pigment involved in photosynthesis
Characteristics of chlorophyll
Chlorophyll appears green because it can absorb the violet, red and blue light, while it reflects the green light. For this reason, the leaves and tender parts of the plants show the typical green color.
Similarly, in autumn, when plants chlorophyll breaks down in many plants, their leaves turn brown, red or brownish.
From a viewpoint of natural medicine, chlorophyll is very important to treat many diseases.
Properties of chlorophyll
- From a vegetable perspective chlorophyll is necessary for the process of photosynthesis.
- From a natural point of view, chlorophyll is used as an anticancer, antioxidant and energizing component.
The chlorophyll molecule
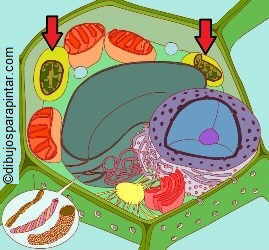
Drawing of plant cell with chloroplasts indicated by red arrows. Inside chloroplasts, there is is chlorophyll, which transforms light energy into chemical energy.
The chlorophyll molecule is made up mainly of carbon and hydrogen. In the center of this molecule there is a single nitrogen atom surrounded by a ring of porphyrins.
The touch of light particles (photons) with chlorophyll produces its excitation triggering a series of photochemical reactions that are in charge of transforming light energy into chemical energy.
Where is chlorophyll located?
Chlorophyll is located in the chloroplasts that are small flattened tiny granules, which usually appear in the cytoplasm near the cell wall. Inside the chloroplasts photosynthetic pigments can be found surrounded by a transparent base substance.
Types of chlorophyll
- Chlorophyll a (C 55 H 72 O 5 N 4 Mg): It is the most common type of chlorophyll, as the 3 / 4 of green chlorophyll belong to this type.
- Chlorophyll b (C 55 H 70 O 6 N 4 Mg) Less common than chlorophyll a. It appears in plants, green algae and other organisms and some cyanobacteria.
The other types of chlorophyll are less frequent, such as chlorophyll c1 and chlorophyll c 2 that appear in red algae and some primitive algae. Chlorophyll d is even more exclusive, appearing in the cyanobacterium (Acaryochloris marina) and seaweeds.
![]() More information on the natural properties of chlorophyll
More information on the natural properties of chlorophyll