Contents
What is a carob tree?
Characteristics of carob tree (Ceratonia siliqua)
Botanical classification | |
Kingdom | Plantae – Plants |
Subkingdom | Tracheobionta |
Superdivision | Spermatophyta |
Division | Magnoliophyta or Angiosperm |
Class | Magnoliopsida or Dicotyledonous |
Order | Fabales |
Family | Fabaceae |
Gender | Ceratonia |
Species | C. siliqua |
Common English noun: Carob, Carob tree, St. John’s bread, Locust tree
* See: Carob tree in other languages
Scientific noun: Ceratonia siliqua L.
Family: Pea family – Fabaceae or Leguminosae
Habitat
Cultivated in the Mediterranean warm regions of calcareous soils and naturalized in dry, rocky places not very far from the sea.
Distribution
Widely spread throughout the Mediterranean region. It is currently found in many countries with Mediterranean-like climates, such as North and South Africa, some regions of the United States and Australia.
Description of Carob tree
A Perennial tree of the Pea family – Fabaceae – up to 10 m. The roots of carob are very deep, capable of capturing the groundwater accumulated during the winter, so it can resist times of drought
This is generally a dioecious tree, that is to say male and female samples appear in different plants, although it can also be hermaphrodite.

Photo of carob general aspect
Smooth stems,with many protuberances, grayish.
Alternate leaves, composite with paired leaflets, from 10 to 20 cm. long. Leaflets 3-5 cm, bright green above, coriaceous, with short stalk.

A detail of carob leaves
Flowers without corolla, of three different types: male (only with five stamens), female (with a single pistil) and hermaphrodite (a combination of both previous elements). Flowers are pollinated by wind and insects.
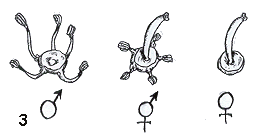
A drawing of the flowers (male, hermaphrodite and female)

A detail of a hermaphrodite flower with a lot of stamens surrounding the pistil
The fruit is a pod, indehiscent, till 25 cm long, dark brown in full maturity.
Carob fruits
Inside it contains the seeds, which are rich in mucilages and galactomannans. From these seeds you obtain a food thickener called locust bean gum (formerly called carubin).

Photo of broken fruits with seeds
Picking-up and storing Carob
Pods must be collected at the end of summer or beginning of autumn if they are needed to be dry. If you want them unripe, you can collect them in mid spring. Bark is always available.
Components of carob tree
- Tannins (Leaves and bark)
- Fiber: Cellulose, hemicellulose, galactomannans, mucilages and gums (Seeds), Cellulose (Fruits and seeds), Pectin, xylose, galactan, pentosan,
- Carbohydrates: Sucrose or sugar, starch, pinitol, fructose, glucose, (fruit)
- Proteins (Seeds): Carob flour (including fruit and ground seeds) contains approximately 5% protein. It stands out because 60% of its content in amino acids consists of aspartic acid, glutamic acid, alanine, glutamine, leucine and valine. It also provides lots of arginine, lysine, glycine, proline, tyrosine, phenylalanine.
- Fats: (Fruits and seeds): mainly linoleic, oleic and stearic acids.
- Minerals: Potassium, calcium, magnesium, iron, manganese, zinc and copper.
- Salicylates (Seeds): with anti-inflammatory, febrile and uricosuric properties
- Flavonoids: Quercetin, gallic acid, proanthocyanidins and tannic acid derivatives
- Saponins (Fruit)
- Beta sitosterol (Seeds)
USES OF CAROB
Carob as as curative plant
Carob tree has been used as a medicinal tree, mainly with the following applications:
- Laxative: Seeds, very rich in mucilages, and specially pods, mainly tender ones, are very good for constipation..(Decoction of 30 gr. of pod pieces in a litre of water for 30 minutes. Sieve and drink the desired quantity)
- Astringent: This plant, very rich in tannins, may be used in a different opposite way to the one previously mentioned, being a good remedy for diarrhea (decoction of 50 gr. of bark per litre of water. Drink 4 cups a day.)
- Kidney failure: Carob tree, when it is mixed in bilberry juice, stimulates the lazy kidneys.
* More information on medicinal properties of carob.
Other uses of Carob
Its fruit can be used as a substitute of cocoa in the chocolate preparation or making cakes with its flour can be a good solution to fight intestinal illnesses.
- Animal food: Carob beans are used to feed livestock. When they are dry, they are very appreciated by horses. They are also a component of fodder.
- Food thickener: food industry makes a good use of this fruit as a thickener.
![]() More information on carob.
More information on carob.









