Contents
What is a caraway plant?
Characteristics of caraway (Carum carvi)
Common English name: Caraway, meridian fennel, Persian cumin
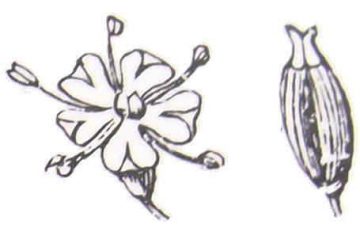
 Caraway fruits
Caraway fruits
Scientific name: Carum carvi
*See: Caraway in other languages
Family: Apiaceae or Umbelliferae
Origin: Northern and Central Europe.
Habitat: It requires fertile, well-drained, light soil for proper growth. It does not tolerate moisture or clay soils., preferring chalky soil, wit a pH 7 or 7.5.
Geographical distribution: It has now been naturalized in all continents. It is mainly found in mountainous areas up to 2,000 m., Distributed through Europe, Siberia, the Caucasus and Central Asia. In general, caraway is not in the Mediterranean due to warmer weather.
Caraway description

Caraway (Carum carvi) is an annual or biennial herbaceous plant, 30-70 cm tall.
It has a pivotal taproot, yellowish, from which numerous erect stems spring. They are erect, cylindrical, branched and striated.
The leaves are arranged alternately to the stem, petiolated. The foliage is divided into pinnate or bipinnate leaves. The upper leaves may be sessile.
The inflorescence is a terminal umbel with tiny white flowers. Each umbel may contain between 6 and 14 unequal radiuses. This is an umbel, a very characteristic inflorescence of the Asteraceae family. It is shaped like an inverted umbrella, which is formed because all the flower stalks are joined to the stem by the same point.
Used parts of caraway
- Root: the root is eaten boiled, steamed, in soups or puree. It can also be cut and fried in the same way as potatoes.

An enlarged detail of the flower and the fruit of caraway Leaves: fresh young leaves are used in salads.
- Flower stalks: The flower stalks are eaten as if they were asparagus in North Africa.
- Seeds or fruits: Small fruits are used as a condiment (alone or in blends like curry), and in phytotherapy.
- Essential oil: It is used in aromatherapy, perfumery and as a flavoring additive.
Composition of caraway
- Carbohydrates

Flowers in umbel of caraway Protein
- Fats
- Fiber
- Vitamins: It contains B vitamins and small amounts of vitamin C.
- Minerals: calcium, magnesium, manganese, chromium, potassium, iron.
- Beta-carotene
- Quercetin
- Furfural (antiseptic)
- Essential oil (3-6%): Carvone (50-60%), dyhydrocarvone, carveol, dihydrocarveol, limonene, acetic aldehyde.
Caraway essential oil (aromatic components)
 Caraway leaves
Caraway leaves
- Terpenes: carvone (carminative, antioxidant, stimulant, vermifuge). Caraway is one of the richest plants in carvone.
- Monoterpenes: limonene, gamma-terpinene, myrcene, acetaldehyde, carveol, cis-carveol, trans-carveol, alpha-phellandrene, alpha-pinene, alpha-terpinene, linalool, beta-pinene, carvacrol, thujene.
- Sesquiterpenes: cadinene, camphene (expectorant)
- Tannins: The plant contains tannins (antioxidant and astringent)
| Composition of caraway seed per 100g. | |
| Nutrient | Amount |
| Energy/ Calories | 333kcal. |
| Carbohydrates | 49,90g. |
| Proteins | 19,77g. |
| Fats | 14,59g. |
| Fiber | 38g. |
| Vitamin C | 21mg. |
| Thiamin | 0,38mg. |
| Niacin | 3,60mg. |
| Iron | 16,23mg. |
| Calcium | 689mg. |
| Phosphorus | 568mg. |
| Magnesium | 258mg. |
| Potassium | 1.351mg. |
| Sodium | 17mg. |
| Selenium | 12,1mg. |
| Phytosterols | 76mg. |
| Aromatic components of caraway | |
| Carvone | 44.310ppm. |
| Limonene | 30.180ppm. |
| Gamma-terpinene | 14.160ppm. |
| Carveol | 3.240ppm. |
| Myrcene | 1.560ppm. |
| dyhydrocarvone | 1.500ppm. |
| Cadinene | 3.720ppm. |
| Camphene | 900ppm. |
| Beta-pinene | 600ppm. |
| Alpha-pinene | 540ppm. |
| Botanical classification | |
| Kingdom | Plantae |
| Subkingdom | Tracheobionta Vascular plants |
| Superdivision | Spermatophyta Seed plants |
| Division | Magnoliophyta Flower plans |
| Class | Magnoliopsida Dicotyledons |
| Order | Apiales |
| Family | Apiaceae |
| Gender | Carum |
| Species | Carum carvi |
![]() More information about caraway.
More information about caraway.