Contents
What is a Brazil nut tree
Characteristics of a Brazil nut tree (Bertholletia excelsa)
Common English name: Brazil-nut Tree, Para Nut, Brazilnuts (fruit), Juvia (tree)
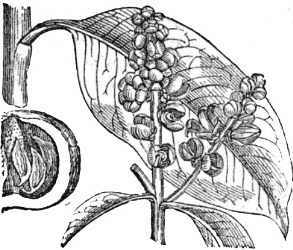 Illustration of Brazil-nut tree Illustration of Brazil-nut tree |
Scientific name: Bertholletia excelsa Humb. & Bonpl.
* See: Brazil nut in other languages
Family: Lecythidaceae
Distribution: The tree grows naturally in the Amazon forests of Brazil, Bolivia and Peru. Introduced in Malaysia, Sri Lanka, Java, Hawaii and the Caribbean.
Habitat: It grows in deep, well-drained alluvial soils on high ground. It does not tolerate flooding.
Description of Brazil-nut tree
Large tree, 30 to 50m high. The base of these trees can reach 2m wide.
Dark green leaves, oblong, 30 to 50cm in length.
Flowers solitary or in clusters, small, about 2 cm in diameter, yellowish.
The fruit is a globose, woody capsule (pixidium), with a shape and size similar to an orange, between 8-15cm in diameter (The natives call this capsule “ouriços”). When mature, it releases the seeds found inside. A fruit may contain between 14 and 24 seeds, hard shelled, 4-7cm long. By breaking this shell, Brazil nuts or coquitos are obtained.
Brazil nuts uses
- It is mainly used to produce seeds, Brazil nuts. For centuries, it has been an important food for many Amazonian tribes. It is currently marketed as a dried fruit.
- Brazil nuts can be used for ice cream, pastries, sweets, desserts, etc. With its seeds, a vegetable milk, known as chestnut milk (Leite castanha), is made.
- You can get Brazil nut oil, which is rich in linolenic acid and has cosmetic properties to beautify the skin. The extraction residue is a flour rich in proteins that, combined with wheat flour, is used for making bread. It can also be used for animal feed.
- Tree wood has a reddish-brown color and can be used to make furniture, but felling of these trees is prohibited (by law) in some countries.
- The capsule fruit (pixidium) is used to burn, or for local craft work (boxes, ornaments, mortars, etc.).
Composition of Brazil nuts
Brazil nuts are very rich in plant seeds proteins, essential fatty acids, fiber, potassium, phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, selenium and vitamin E.
They are the richest nuts in magnesium and the richest in selenium of all food.
The following table shows the composition of Brazil nuts per 100 grams per serving shown:
| Nutritional composition of Brazil nuts | ||
| Per 100g | Per serving 20g.(4-6 seeds) | |
| 3,34 | 0,67 | |
Calories | 656 | 131,2 |
| 66,22 | 13,24 | |
| 14,34 | 2,87 | |
| 12,80 | 2,56 | |
| 5,4 | 1,08 | |
| 600 | 120 | |
| 600 | 120 | |
| 3,40 | 0,68 | |
| 2 | 0,4 | |
| 225 | 45 | |
| 176 | 35,2 | |
| Zinc (mg.) | 4,59 | 0,92 |
| Selenium (mcg.) | 2960 | 592 |
| Vitamin C (mg.) | 0,7 | 0,14 |
| Vitamin A (UI) | 0 | 0 |
| Folic acid (mcg) | 4 | 0’8 |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamin) (mg.) | 1 | 0,2 |
| Vitamina B2 (Riboflavin) (mg.) | 0,122 | 0,02 |
| Vitamin E (mg.) | 7,6 | 1,52 |
| Pantothenic acid (mg.) | 0,236 | 0,05 |
| Niacin (mg.) | 1,622 | 0,32 |
![]() More information on Brazil nuts
More information on Brazil nuts








