Contents
What is a black mustard?
Black mustard characteristics ( Brassica nigra)
Common English name: True mustard, black mustard, common mustard
Etymology: The term ‘mustard’ derives from the Latin “Mustum ardens”, which literally means “burning grape must”. This derives from an ancient preparation made with grape juice and mustard, that had a burning taste.
Scientific name: Brassica nigra (L.) W.D.J. Koch.
Taxonomic synonym: Brassica bracteolata Fisch. & C.A.Mey. Brassica sinapioides Rothm. Sinapis nigra var. turgida Pers. Sinapis nigra L. Sinapis tetraedra C.Presl in J.Presl & C.Presl. Sinapis gorraea Wall. Sinapis bracteolata G.Don in Sweet. Brassica melanosinapis Endl. Brassica brachycarpa Candargy. Sinapis incana Thuill. Sisymbrium nigrum (L.) Prantl. Mutarda nigra (L.) Bernh. Melanosinapis communis Spenn. Erysimum glabrum C.Presl. Sinapis tetraedra J.Presl & C.Presl] Crucifera sinapis
*See: Black mustard in other languages
Family: Brassicaceae, or Cruciferae
Habitat black mustard
Common mustard is a plant native to Eurasia, from Southeast Asia. It grows throughout Europe, except the northern and eastern regions; in Siberia, Asia Minor and North Africa. Naturalized in North and South America.
In these regions, we can find common mustard on uncultivated land, roadsides, cultivated land, ravines, meadows and streams, where this plant is native.
It is widely cultivated in England, Holland, Italy and Germany. The interest lies in its seeds, which are an aromatic spice widely used worldwide.
Botanical characteristics of Mustard
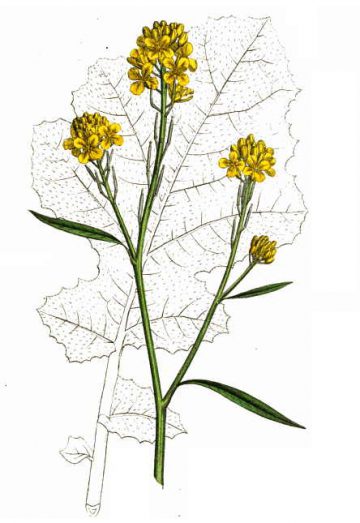
Botanical illustration of black mustard (Brassica nigra).
Black mustard (Brassica nigra) is an annual plant of the Brassicaceae family, a relative of the cabbage and arugula. Its size varies between 50 and 100 centimeters tall. Stem erect, smooth, branched with rough hairs towards the base.
Alternate, petioles and large leaves at its base. Divided by serrated margin segments. The lower leaves are divided into segments and the terminal deep lobe is superior to others. The upper leaves are less divided or whole, also with shorter petiole. The leaves of the black mustard are not sessile, which makes it different from Indian mustard (Brassica juncea).
The inflorescence is a flower cluster Mustard flowers are stalked, yellow, formed by four crossed petals (characteristic form of Brassicaceae or cruciferous plants). The calyx consists of four equally crossed sepals. It contains six stamens, of which 4 are longer. These flowers give off a pleasant scent.
Black mustard blooms from June to September.
The fruit of mustard plant is a nut in structure or dried leguminous silicua. It is long, slender and erect, thinner at the end forming a peak of 4-5 mm and attached to the stem. Inside, it contains between 8 and 12 reddish brown seeds with a size between 1 to 1.2 millimeters in diameter.

In the picture: petal (1), flower (2), fruit (3) and seed (4) black mustard (Brassica nigra)
What parts of mustard are used
- The tender leaves of the plant are edible. They are collected in early spring. They contain antioxidants and anticancer substances but they should be eaten in moderation as food because of its content in oxalates.
- Mustard seeds are the most used parts of the plant. The ground seeds (“mustard flour”) are used in the preparation of medicinal baths and cataplasms, called poultices (the word ” sinapism ” comes from the Greek sinapis, meaning mustard).
- They are also used in food to prepare hot sauces that are used as condiments.
What does black mustard contain?
One of the most important components of black mustard is sinogroside, a glucosinolate that gives it its peculiar taste and most of its properties. (More information: Black mustard composition)
![]() More information on black mustard
More information on black mustard