Contents
What is an avocado plant?
Avocado characteristics (Persea americana)
Common English name: Avocado (tree) Avocado, Alligator pear (fruit). The word “avocado” comes from the Spanish aguacate
– Spanish / Castellano: Aguacate, palta.
The word “aguacate” comes from the Nahuatl “ahuacatl” (= testis)
The word “palta” comes from the Quechua and refers to the paltas, people living in a region north of Peru and southern Ecuador.
Scientific name: Persea americana L.
– Synonyms:Persea drymifolia, Persea edulis, Persea gigantea, Persea gratissima, Laurus persea, Persea nubigena, Persea persea,
Family: Lauraceae
Origin: It is native of Central America (Mexico and Guatemala), where it was already cultivated before the arrival of the Spaniards and was highly prized among the Maya and Aztec people.
Distribution: Today appears cultivated in many American countries, the main: United States, Mexico, Brazil, Kenya, South Africa, Israel and Spain.
Habitat: It is a plant that requires a very warm climate, so, in certain places, it should be grown in greenhouses.
Description of the avocado plant

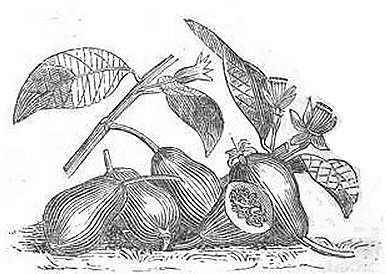
Illustration of a branch of avocado
Avocado (Persea americana), is a tree of the Lauraceae family, to which belong some species as well known as laurel, cinnamon tree (Cinnamomum verum) or camphor tree (Laurus camphora).
Avocado can about 20 m. tall, although, when cultivated, it is not allowed to grow more than 5 m.
Its leaves are evergreen, large (7 -. 40 cm long), dark green on the back and lighter on the bottom color.
Its flowers are green, very small and its trunk is rough brown.
Avocado fruit is a pear-shaped drupe, olive green, with a rough surface and yellowish green flesh, surrounding a very large central seed (There are varieties that do not have seeds).
There are approximately 400 varieties, so we can find fruits of different shapes and weights, which can reach up to 2 kg.
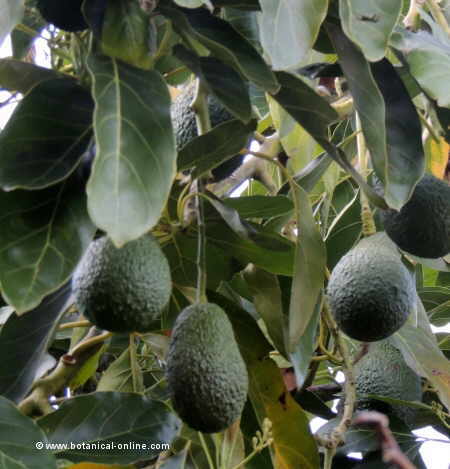

Photo of avocado (Persea americana), with the fruits and the leaves
Avocado composition
– Carbohydrates (8%)
– Protein (2%): tryptophan, alanine
– Fat (7%): of which monounsaturated (77%), polyunsaturated fats (13%) and saturated fat (10%)
– Fiber (5%)
– Minerals: Potassium, magnesium, copper, iron, zinc, manganese, selenium
– Vitamins: riboflavin, thiamine, niacin, vitamin A. High in pyridoxine, vitamin E and folacin in fruits.

Photography of avocados
– Essential oil: Anethole (bark), perseitol (seeds)
– Organic acids: chlorogenic acid (fruit), tartaric acid (fruit)
– Phytosterols (fruit)
– Flavonoids: Quercetin (leaves), zeaxanthin (fruit)
![]() More information on avocado
More information on avocado