Contents
What are lions?
Characteristics of lions
Common name: Lion
Scientific name: Panthera leo

– Scientific classification:
Class: Mammalia
Order: Carnivora
Family: Felidae
Features:
- Length: 2’20 – 3 m.
- Heigth: Up to 1’10 m males. Up to 0’85 m females.
- Weight: Up to 225 kg.
- Habitat: African savanna.
- Geographic range: Sub-Saharan Africa.
- Food habits: Carnivore (wildebeest, gazelles, buffalos, giraffes, large antelopes, carrion).
- Behavior: Terrestrial, gregarious, territorial, diurnal, nocturnal.
- Reproduction: Viviparous. Gestation: 3 months. Birth: 3 babies.
- Enemies: Humans.
- Lifespan: Between 5 and 15 years, according to sex.
Physical description of lions

Lion males and lionesses are quite different from each other. While males have a long mane, lionesses does not possess this attribute. In addition, the head of lion males is larger than that of females.
Asian lion are physically different from African lions by presenting a long fold of skin in the abdominal area.
Lion behavior
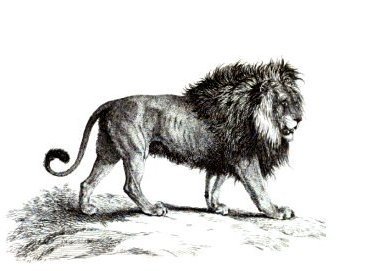
Lions have a very powerful roar capable of being heard more than 8 km away. With their powerful roars, these wild animals warn intruders that are within its territory or serves to communicate with members of their clan.
While lionesses are good hunters, the great weight of male lions prevents them from hunting. The function of males is to defend the territory of rival groups.
Some lions can climb trees, with the aim of freeing themselves from the intense heat of the African plain. They also do it to avoid the annoying parasites.
In fact, there are cases of lions that are forced to migrate to quieter areas because of tick-biting and other annoying invertebrates.
Lion food habits
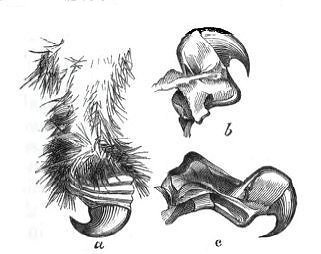

Although lions feed on a wide variety of prey, they can also eat carrion.
When usual lion preys migrate to the most favorable areas during the dry season, these animals are forced to hunt other preys and carrion becomes a very important source of food.
For hunting, lions are equipped with retractable claws. Because lion claws are retractable, these animals can run without having to wear away their nails and use them for hunting at just the right time.
Lion reproduction

Where do lions live?
Lions live in African savannas as cheetahs do, although most felines live in jungles or forests, such as tigers, leopards or jaguars.
Other wild felines prefer mountain areas, such as pumas, although they can live in lowlands.
Lion enemies
Lions have no natural enemies, to the point that the deaths of lion cubs are often caused by the attack of another male lion either from a rival group or even from a male of the same family group.
![]() More information on other wild animals.
More information on other wild animals.







