Contents
Botanical characteristics of Cactaceae
Cactus family characteristics
Cactaceae plants
The cactus family – Cactaceae – includes about 2000 species of plants distributed in places of desert or very dry climate, mainly in Central America and South America, although they have been introduced and adapted to other places of dry and warm climate, as Australia, the Mediterranean and East Africa.
More rarely we meet with epiphytic species (those that live at the expense of other plants) adapted to live in forests of humid climates.
Importance of the cactus family in the world
CACTUS AS FOOD:


Broadly used as human food, most of the cactus family members, with the exception of those belonging to Pereskia genera, are used as food mainly by their fruits.
For example the fruits of the Opuntia ficus-indica (prickly pear), whose berries were in fact fundamental during the trips of the Hispanic settlers to America like a source of food to avoid the scurvy, are also eaten up at the moment in the Mediterranean region, where the peculiar climatic characteristics have supposed a perfect adaptation of the plant, being of particular interest in the island of Sicily, Tunisia, Algeria, Morocco, Turkey and Israel.
In central America the species of Opuntias used, besides the previous one, it is very numerous from the Opuntia megacantha var. jitomatilli that is used instead of the tomatoes until the Opuntia robust var. robusta whose barks are eaten up fried, instead of chips. Many more genera of cactus are used as food such as Acantohocereus, Cephalocereus, Hylocereus..etc. Apart form the fruits the seeds are also consumed roasted or crushed to prepare cakes.
LIVESTOCK:
Many cactus are cultivated or harvested in the wild because of its leaves to feed the livestock – Cephalocereus, Ferocactus, Mammillaria…etc. and they constitute a fundamental resource when being in very arid areas where the presence of more” tender plants” is practically null.
Many of these species are useful to build fences where to keep the animals or to separate the fields.
SOIL PROTECTION:
In arid and windy places they are used to fix the floor and to prevent the erosion of the rain that usually takes place in a torrential way during some periods of the year. This use becomes very appropriate in the cultivations that are carried out in form of terraces.
MEDICINES AND POISONS:
Some of them are well-known worldwide because of their medicinal or toxic properties, as peyote (Lophophora willamsii) for its hallucinogenic properties.
GARDENING:
Admired by their attractive flowers, their extravagant forms or their bristled spikes, they have been broadly exploited in gardening, which has carried many of them to the edge of extinction.
Very well-known in the world of the gardening we would have:
| Apple cactus | Barrel cactus | Christmas cactus |
 |  |  |
| Cereus peruvianus monstruosus | Echinocactus grusonii | Hatiora gaertneri |
To see more plants of this family as well as the cultivation tips ![]()
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE CACTUS FAMILY
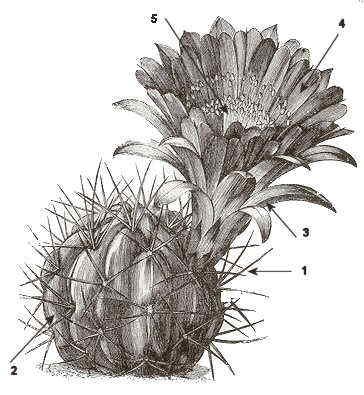 Leaves (1): Simple, alternate, generally transformed in prickles. Only Pereskia and Pereskiopsis genera show well developed leaves
Leaves (1): Simple, alternate, generally transformed in prickles. Only Pereskia and Pereskiopsis genera show well developed leaves
Stems (2): Succulent., more rarely ligneous. Sometimes formed with superimposed cladodes. They distinguish themselves because of the areolae, that are the zones where prickles grow. Areolae are equivalent to branches in the rest of the plants. Flowers: Big, solitary with radial symmetry – actinomorphic – more rarely with bilateral symmetry – zygomorphic
Calix (3):With many petaloid tepals.
Corolla (4): With many sepaloid tepals, surrounding the petaloid ones.. Both of them as a result of the evolution of the initial bracts.
Stamens (5): Many
Ovary: inferior.
Carpels: 3 o more
Fruit: Fleshy
*Illustration: Echinopsis pentlandi Scheerii
CACTUS GENERA PLANTS
It is thought there are about 200 genera. The more important ones are the following:
| ACANTHOCALYCIUM ACANTHOCEREUS APOROCACTUS ARIOCARPUS ARMATOCEREUS ARROJADOA, ARTHROCEREUS ASTROPHYTUM AUSTROCACTUS AZTEKIUM BERGEROCACTUS BLOSSFELDIA BRACHYCEREUS BRASILIC BROWNINGIA CALYMMANTHIUM CARNEGIEA CEPHALOCEREUS CHAMAECEREUS CIPOCEREUS CLEISTOCACTUS COLEOCEPHALOCEREUS COPIAPOA CORRYOCACTUS CORYPHANTHA DENMOZA DISCOCACTUS DISOCACTUS ECHINOCEREUS ECHINOPSIS EPIPHYLLUM EPITHELANTHA ERIOSYCE ESCOBARIA ESPOSTOA ESPOSTOOPSIS EULYCHNIA FACHEIROA FEROCACTUS FRAILEA GYMNOCALYCIUM HAAGEOCEREUS HARRISIA HATIORA HELIOCEREUS HYLOCEREUS | JASMINOCEREUS LEOCEREUS LEPISMIUM LEPTOCEREUS LEUCHTENBERGIA LOPHOPHORA MAIHUENIA MAMMILLARIA MELOCACTUS MICRANTHOCEREUS MILA MYRTILLOCACTUS NEOLLOYDIA NEOPORTERIA NEORAIMONDIA NEOWERDOMANNIA OBREGONIA PACHYCEREUS PARODIA PEDIOCACTUS PELECYPHORA PENIOCEREUS PERESKIA PERESKIOPSIS, PILOSOCEREUS PSEUDORHIPSALIS PTEROCACTUS, REBUTIA RHIPSALIS SAMAIPATICEREUS SCLEROCACTUS SELENICEREUS STENOCACTUS STENOCEREUS STEPHANOCEREUS STETSONIA STROMBOCACTUS TACINGA THELOCACTUS UEBELMANNIA WEBERBAUEROCEREUS WEBEROCEREUS ZYGOCACTUS. |
![]() More information about plants.
More information about plants.